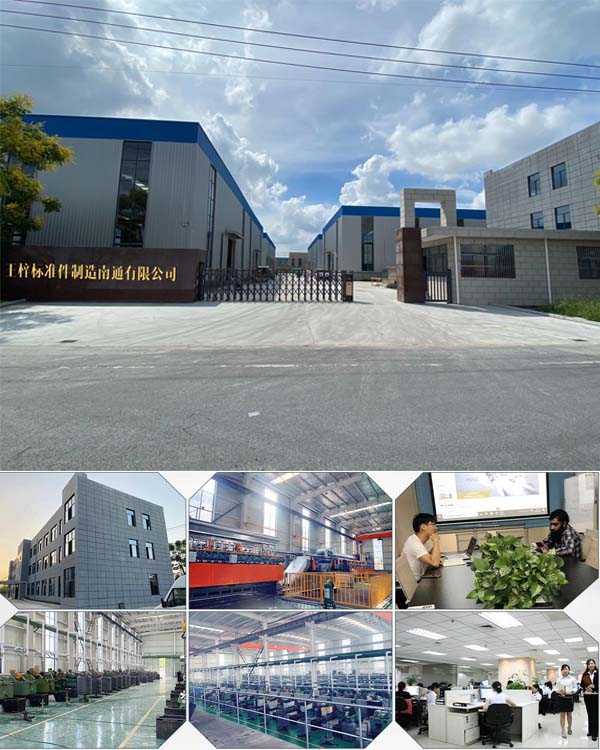
How Is a Screw Produced?
Screws and bolts are similar fasteners, usually made of metal, featuring a helical ridge called an external thread (male thread). Screws and bolts are used to fasten materials whose purpose is to engage the threads with a matching portion of similar internal threads (female threads).
Generally self-tapping (also known as self-tapping wire), when the screw is rotated, the threads cut into the material, creating an internal thread, which helps pull the tight material and prevents pull-out. There are many kinds of materials that screws are usually used to secure, including wood, sheet metal, and plastic.
4 common materials of screws.
Screws can be made from many different materials, but some are better than others. The four most commonly used screw materials are.
Steel: This is by far the most common material used to manufacture screws for one simple reason: steel is cheaper than certain other screw materials.
Copper: Copper screws are good for corrosion protection. If you want to contact different components, copper can ensure a long life of the screw.
Aluminium: Aluminum is not as durable as other materials, but it does have one advantage – weight. Aluminium is the lightest fastener you can find.
Titanium: When you need both strength and lightness, choose titanium. Titanium screws are expensive, but if you need a strong yet not heavy fastener, the extra cost can pay off handsomely.

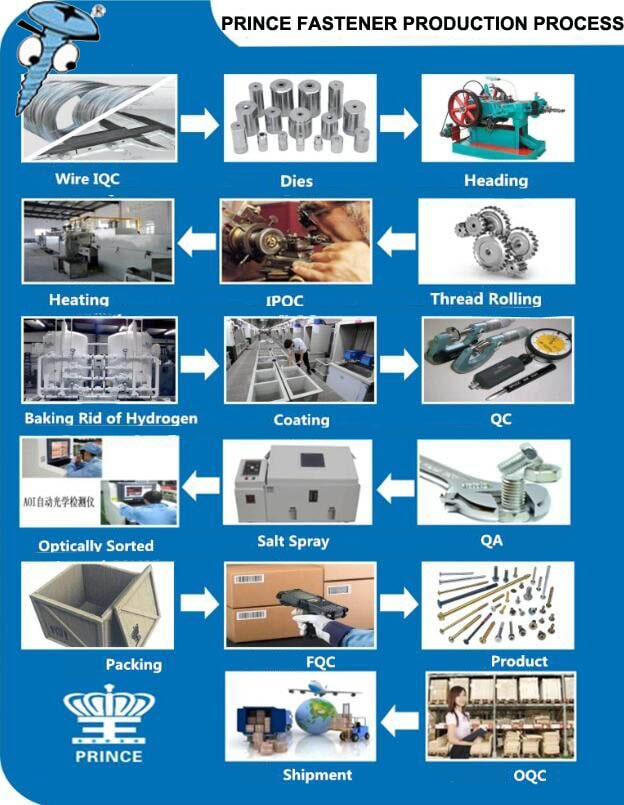
Prince fastener production process
Basic concepts of Prince Fastener screw production
1,Prince Fastener Manufacturing screw can be divided into a cold heading, hot machining (turning, milling, etc.)
2,Cold headings are the use of plastic metal, by using cold mechanical pressure or drawing, reaches the solid metal deformation.
Cold forging begins with a large steel wire, which is uncoiled and cut to a certain length. The ISO 8981 standard specifies that the grade of steel has been standardized in the industry. With special tools, the wire is cold forged into the right shape. Basically, the steel is formed at room temperature and forced through a series of dies under high pressure. The tool itself can be complex and include up to 200 different parts with a tolerance of 1% mm. With improvements, cold forging ensures that bolts can be produced quickly, in high volume and with high uniformity.
For more complex bolt designs that cannot be cold-forged and shaped alone, some additional turning or drilling may be required. Turning involves rotating the bolt at high speed while cutting the steel to obtain the desired shape and design. Drilling machines can be used to drill the bolts. Some bolts can also be fitted with washers during the process, if necessary.
3,Hot upsettings are the material after heating and pressure processing make the shape of the material meet the design requirements.
For all bolts, heat treatment is a standard process that involves subjecting the bolt to extreme temperatures to harden the steel. The bolts are typically rolled or cut when the steel is softened prior to heat treating. Rolling works very similar to cold forging and involves threading the bolt into a die that shapes and moulds the steel into threads. Cutting is done by cutting and removing the steel to form the threads.
Because heat treatment changes the nature of the steel and hardens it, pre-threading is easier and more cost-effective. However, heat-treated threads mean better fatigue performance. “Princefastener explains that heat treatment can lead to thermal cracking and minor damage to the bolt. “As a result, some customers require heat-treated threads, especially for applications such as engine and cylinder head bolts. This process is more expensive because it requires the generation of hardened steel, but it protects it better.”
4,Prince Fastener Machining is a small batch of special or special bolts of the six corners of the head that are turned into after the milling.
5, Screw bolt thread: mechanical and manual threading, similar to die.
6, Milling tail: generally completed by the end of the Prince Fastener cutting machine.
7, The difference between cold and hot upset: cold heading bolts` surfaces are more beautiful, dozen red bolt surface oxide skin does not look good; cold heading high production is efficiency; general Prince Fastener M24 bolts will need to play red;
Analysis of the causes of the phenomenon and the causes of the forming process
1,Eccentric: two red and improper installation and adjustment machines.
2,Minow: a poor installation and improper Prince Fastener adjustment machine at.
3,Head is not round: the choice of a die or a punch forming is not enough.
4,Play the mode of crack: crack or die R angle, so that the model is hit by the two collisions.
5,Head double bad punch.
6,Flash: a bad punching moulding is mainly between punch and dies hole clearance is too large or too short by red bars.
7,、Crack angle: the punch needle burst or two punch and punch is not heavy.
8,Head cracking: material, or a die using error (such as pan head Hexagon washer head of a die), and lubricating oil.

Analysis of adverse phenomena and causes of common rolling
1,Processing crack: tooth plate and adjust the Prince Fastener old machine.
2.Blunt tail: the machine is not properly adjusted, the tooth plate is too old.
3,Crooked tail: the control screw on the seat board seat is too tight.
4,Tail: tooth wear plate and improper adjustment machine.
Guidelines and Models
According to the fastener thread standards described in ISO 68-1. ISO 261.
There are many screws and bolts, which can be divided into several categories depending on their use and shape. One is as follows.
Wooden screws are suitable for standard DIN97 and various lower heads (flat head. Oval head . Phillips head. Phillips head. Allen type head. Torx. head).
Square head screw: these are used to fix heavy objects. To DIN571 standard. Self-tapping or threaded moulded screws have threads specifically designed for tapping threaded holes. These materials should not be used hard. din7970.iso1478.bs4174.
Machine Screws: Mechanical screws have finer threads than wood screws. They are designed to fit into nuts or tapped holes.DIN7985, ISO7045, DIN965, DIN966, DIN84, DIN85, DIN933, DIN931, DIN912.
Sheet metal screws are usually short and have coarse threads, and are used to secure relatively thin sheet metal. din7981, iso7049, din7976, din7983, din7971, din7504.
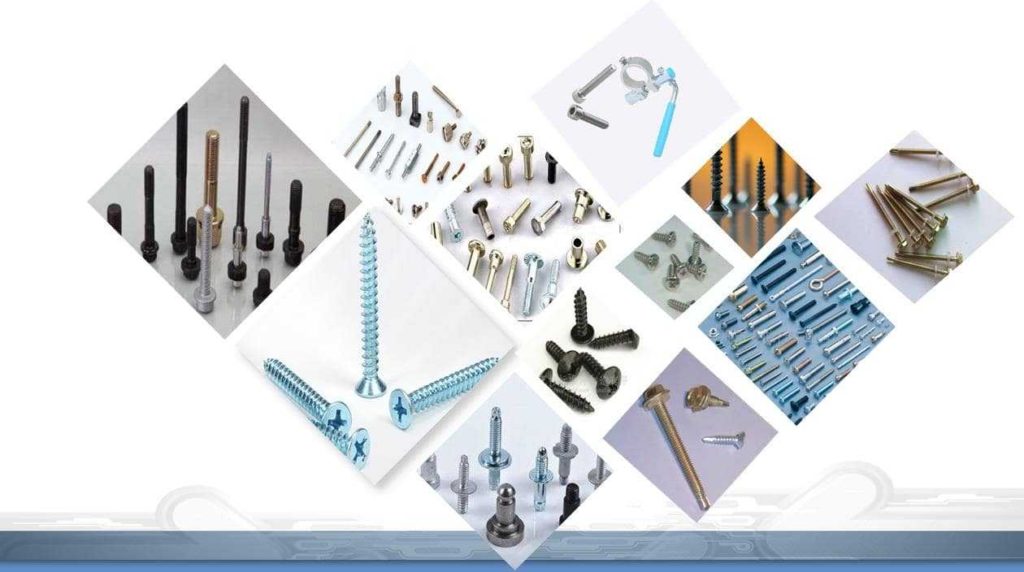

Demand for screws shows no sign of slowing down, but where do they come from?
It’s an alarming world. With 2.5 million fasteners used on every Boeing 747 due to rapid technological advances, the global demand for threaded fasteners continues to grow. The screw manufacturing process has evolved to stay fast, efficient and ahead of the curve; however, its core component, the screw manufacturing process, has remained virtually unchanged for the past 300 years.
Screws can be designed for countless mounting options, including specialized end and drive styles. Fine pitch. Right or left-handed, and flat or screw points, to name just a few. Specific steps in the manufacturing process can be as variable as the screws themselves, but in the modern world, fastener manufacturing can generally be divided into two types, which differ in the methods they use to process threads: rolled screws and thread-cutting screws.
The earliest metal screws in the ancient past were a breakthrough in contemporary engineering. This new invention added helical teeth to the nail, creating an unparalleled industrial fastener. The screw was particularly well suited to gunsmithing because it resisted the vibrations in gunfire. In contrast, parts like nails could (and would) fall out on their own after a period of use, causing guns to go out or even collapse in battle. The earliest screws were carved out of nails and hands.
This meant that any two screws were identical and were produced at a very poor rate and quality. Because of the massive demand, inventors from Europe tried to create devices that would mechanize the screw production process. This effort led Job and William Wyatt to develop a machine that could automatically cut 10 standard screws per minute in 1760.
The screwdriver made by the Wyatt brothers is widely considered one of the first examples of automated mass production, although many specialized screw lathes were screw manufacturers suppliers of screw screws throughout the 18th century. Fastener design and production has progressed considerably since the 17th century and is constantly evolving to improve the versatility of fastener products.
For more information,welcome to send your inquiry to Fastener supplier: Prince Fastener