Prince Fastener will delve into a seemingly simple yet critically important topic—wood screws. Whether in furniture manufacturing, building structures, or woodworking projects, wood screws play an indispensable role. Their unique design and function provide strong support for connecting wooden materials. But do you truly understand the mysteries of wood screws? How do they differ from metal screws? In which situations are they the best choice, and where might they be less suitable? This article will answer these questions one by one, taking you into the world of wood screws to learn about their applications, differences, and maintenance methods in humid environments. Let’s uncover the mystique of wood screws together and explore their importance in modern life.
What Are Wood Screws?
Wood screws, also known as wood bolts, are specifically designed for use on wooden substrates and are widely used in furniture, construction, and woodworking industries. The head types are generally flat head, oval head, or hex head. Slot types are usually slotted or Phillips, which is more common nowadays.
Difference: Wood screws are specially designed screws for wood, quite different from other self-tapping screws in aspects like pitch and thread differences. Visually, wood screws typically have a section of unthreaded shank.
They have the following characteristics:
- Thread Design: The threads of wood screws are specifically designed for wood. They are finer and spaced closer together, which helps reduce the splitting of the wood when screwed in.
- Head Design: The head of a wood screw is usually more extensive, sometimes with grooves, to facilitate screwing in with a screwdriver or drill. Common head shapes include round head, flat head, and oval head. The screw heads are divided into slotted and Phillips types.
- Material: Common materials for wood screws include iron and copper, and there are also stainless steel versions, suitable for different environments and needs.
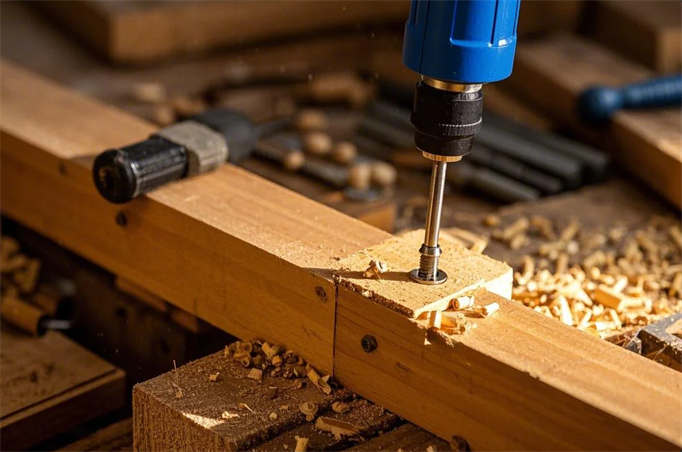
- Usage Method: Wood screws require pre-drilling before screwing in to avoid splitting the wood. During use, a screwdriver should be used to screw them in, rather than hammering, to protect the wood surface from damage.
- Removability: The connection formed by wood screws is detachable, meaning they can be removed and replaced without causing significant damage to the wood.
- Fastening Ability: Wood screws have a stronger fastening ability than nails and are more convenient to use, causing less damage to the wood surface.
- Specifications: Wood screws come in various specifications, including different diameters and lengths, to suit different usage scenarios.
Wood screws are widely used in furniture manufacturing, woodworking, construction, and other fields. They are standard fasteners for connecting wooden components.
What’s the Difference Between Wood Screws and Metal Screws?
Wood screws and metal screws (usually referring to screws used for metal connections) have some significant differences in design and usage:
- Tread Design:
- Wood Screws: Threads are finer and spaced closer together, suitable for the hardness and structure of wood, reducing splitting when screwed in.
- Metal Screws: Threads are coarser and spaced wider apart, accommodating the hardness and strength of metal to ensure sufficient grip in metal parts.
- Material:
- Wood Screws: Usually made of iron, copper, or stainless steel, suitable for different environments and anti-corrosion needs.
- Metal Screws: Typically made of high-strength metals like carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel to withstand greater forces.
- Head Design:
- Wood Screws: Heads are usually larger, sometimes grooved for easy screwing with a screwdriver or drill. Common head shapes include round head, flat head, and oval head.
- Metal Screws: Head designs vary, including hex head, round head, and flat head, to suit different tightening tools and application needs.
- Usage Method:
- Wood Screws: Require pre-drilling before screwing in to avoid splitting the wood.
- Metal Screws: Can be directly screwed into metal holes or used with nuts.
- Fastening Ability:
- Wood Screws: Fastening ability is more potent than nails but relatively weaker, suitable for non-structural connections.
- Metal Screws: Strong fastening ability, suitable for structural connections, capable of withstanding greater forces.
- Corrosion Resistance:
- Wood Screws: If made from stainless steel, they offer some corrosion resistance but generally not as much as metal screws.
- Metal Screws: Especially stainless steel screws, they have excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for outdoor or humid environments.
- Cost:
- Wood Screws: Generally lower cost because wood is a relatively low-cost material compared to metal.
- Metal Screws: The cost may be higher, especially when using special alloys or stainless steel materials.
- Removability:
- Wood Screws: Form a detachable connection, allowing them to be removed and replaced.
- Metal Screws: These can also be removable, but in some cases, such as using self-tapping screws, they may create an irreversible connection.
The primary differences between wood screws and metal screws lie in their design, materials, and applications to suit different materials and environments.
Where Are Wood Screws Suitable for Use?
Wood screws are suitable for various occasions, mainly including:
- Furniture Manufacturing: Widely used in assembling furniture like cabinets, chairs, tables, and beds to fasten metal or non-metal parts with holes to wooden components.
- Building Structure Connections: In construction, wood screws are extensively used for connecting wooden structures, such as fixing wooden frames and connecting wooden elements in outdoor facilities and landscaping.
- Floor Installation: Floor screws are a type of wood screw designed explicitly for fixing wooden floors, suitable for situations bearing larger loads.
- Fixing Decorative Panels and Wall Surfaces: Wood screws are commonly used in construction projects requiring the fixing of wooden frames or decorative panels.
- Hardware Accessories Installation: This is suitable for installing hinges, latches, box locks, door locks, and other hardware accessories.
- Outdoor Wooden Structures: Anti-corrosion wood screws are specially designed for connecting wooden structures in outdoor or humid environments, featuring excellent corrosion resistance.
- Light Wood Frame Systems: Modern light wood frame buildings extensively use wood screws for connections, fostering the growth of the wood screw market.
- DIY Projects and Woodworking Projects: Ideal for personal DIY and woodworking projects, such as assembling bookshelves, workbenches, etc.
Wood screws are favoured for their removability, high load-bearing capacity, and adaptability, making them extensively used in furniture manufacturing, building structures, floor installation, hardware installation, and other fields.
Are There Places Where Wood Screws Cannot Be Used?
While wood screws are highly suitable in many situations, there are indeed places where they are not appropriate or may be less effective:
- Non-Wood Materials: Wood screws are primarily designed for wooden materials. Their thread structure suits the hardness and fibre structure of wood. They may not provide sufficient grip when used on metal, plastic, or hard materials, leading to unstable connections.
- Hard or Dense Materials: Wood screws have relatively shallow threads with wider spacing, which might not offer enough fastening force on hard materials. For example, when working with metal or concrete, specialized metal screws or concrete screws should be used.
- Humid Environments: Although some wood screws made from stainless steel offer corrosion resistance, ordinary wood screws may rust in continuously humid environments, affecting their performance and lifespan.
- Brick or Masonry Structures: In masonry work, masonry screws should be used instead of wood screws. Masonry screws have longer thread lines and different thread patterns tailored to various material types, designed for use without anchor bolts, wall plugs, or alternative spiral anchor systems.
- High-Strength Connection Requirements: Wood screws have relatively lower strength and are suitable only in less demanding applications. Stronger fasteners are necessary in scenarios requiring higher load-bearing capabilities or critical structural connections.
- Fixing Gypsum Boards: Traditionally, specialized screws are used for hanging and fixing gypsum boards. Compared to wood screws, these specialized screws have limitations. If exposed to continuous humidity, they can rust. An alternative is to install flathead screws to minimize the risk of splitting, cracking, and loosening.
In summary, wood screws may not be suitable or effective in non-wood materials, hard materials, humid environments, brick or masonry structures, high-strength connection scenarios, and when fixing gypsum boards. In these cases, choosing fasteners appropriate for specific materials and environments is essential.
Can Wood Screws Be Used on Metal?
Wood screws are primarily designed for connecting wooden structures with metal or non-metal parts. They can be directly screwed into wood, forming a detachable joint suitable for fastening parts with holes to wooden substrates. For metal applications, wood screws aren’t ideal because their threads are tailored to wood characteristics—the threads are deep and widely spaced to ensure good grip in wood.
Metal screws or self-tapping screws have higher thread minor diameters and robust threads, capable of cutting threads into metal, forming tight thread engagement. Therefore, wood screws aren’t suitable for metal connections, especially where higher strength and stability are required.
For metal connections, specialized metal screws or self-tapping screws should be used. These screws are better suited to metal materials, providing more muscular connection strength and stability.
Will Wood Screws Rust in Humid Environments?
Wood screws can indeed rust in humid environments. Here’s some relevant information:
- Effect of Humidity on Metal Products: Humid environments can be detrimental to metal products, including wood screws. Experiments have shown that screws placed in humid conditions rust very quickly.
- Materials of Wood Screws: Wood screws may be made of steel, with or without various metal coatings like black oxide, bronze, yellow zinc, bright brass, or clear zinc. More corrosion-resistant metals like stainless steel, aluminium, or silicon bronze should be used for external applications or corrosive environments.
- Stainless Steel Wood Screws: Stainless steel screws, especially those made from 304 or 316 stainless steel, have excellent anti-rust properties and can maintain anti-rust effects even in ordinary humid environments. For example, 304 stainless steel screws won’t rust even after long-term immersion in fresh water.
- Anti-Rust Measures: To prevent screws from rusting, measures such as using stainless steel screws, surface treatments (like galvanizing, nickel plating, phosphating), applying anti-rust lubricants, avoiding humid environments, and regular inspections and maintenance can be implemented.
Wood screws can rust in humid environments, especially if they’re not made from stainless steel. To reduce rust risk, opt for stainless steel wood screws or adopt appropriate anti-rust measures.
Can Stainless Steel Screws Completely Prevent Rust?
Stainless steel screws have good corrosion resistance due to their chromium content, allowing them to maintain stable performance in various environments. However, this doesn’t mean they can completely prevent rust. Factors affecting their corrosion resistance include:
- Material Differences: Various grades of stainless steel have different corrosion resistance. For example, 304 and 316 stainless steels differ in corrosion resistance, especially in environments with high chloride ion content.
- Surface Treatment: The surface treatment of stainless steel screws significantly impacts their corrosion resistance. Improper or faulty therapies may result in incomplete or damaged protective films, reducing rust resistance.
- Environmental Factors: Even with good corrosion resistance, exposure to humidity, high temperatures, ample oxygen, acidic or alkaline environments, and mechanical wear can increase rust risk.
- Maintenance: Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of stainless steel screws. Regular cleaning, preventing vibration and impact, and anti-rust agents are effective maintenance methods.
Therefore, stainless steel screws cannot wholly prevent rust. Material, surface treatment, environmental conditions, and maintenance influence their corrosion resistance. Choosing the right material, proper surface treatments, avoiding harsh environments, and regular maintenance can maximize their lifespan and minimize rust.
How to Maintain Screws in Humid Environments?
To maintain screws in humid environments, consider the following measures:
- Choose Suitable Materials: Use high-quality alloy bolts and stainless steel bolts like 321 or 316 stainless steel, which contain higher chromium and nickel content to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Surface Treatment Techniques: Apply surface treatments to enhance bolt corrosion resistance, such as hot-dip galvanizing, electro-galvanizing, or Dacromet coating. These treatments effectively prevent moisture contact.
- Keep Dry: Ensure screws are kept dry during storage and use. Avoid placing them in humid environments, especially water immersion.
- Coating Treatment: Apply coatings to form a protective layer on the screw surface, effectively preventing corrosion from oxygen and water. Coating methods include hot-dip galvanizing, cold galvanizing, and painting.
- Use Anti-Rust Agents: In humid or highly corrosive environments, apply appropriate anti-rust agents for protection. Ensure compatibility with the screw material and contact parts when selecting agents.
- Proper Storage: Store screws in dry, ventilated areas without corrosive gases to prevent moisture and contamination. Inspect and rotate them periodically for long-term storage to avoid rust and deformation.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Even with quality materials and advanced treatments, regular cleaning, inspection, and re-lubrication are necessary. Replace or repair screws if rust or coating damage is detected.
- Use Sealed Containers: Store screws in sealed containers to prevent air and moisture ingress, reducing exposure and rust risk.
- Moisture-Proof Packaging: Consider placing each screw in a small bag with a desiccant before storage. The desiccant absorbs moisture, further protecting screw quality.
- Avoid Impact: Prevent screws from hitting other complex objects during storage to avoid surface damage, which can increase susceptibility to corrosion and rust.
By implementing these measures, you can effectively maintain screws in humid environments and extend their service life.
Through this detailed introduction, we believe you now have a deeper understanding of wood screws. From their unique design to the differences from metal screws, suitable application scenarios, and maintenance methods in humid environments, every detail of wood screws deserves our attention. They’re not just tools for connecting wooden materials but are crucial for ensuring structural stability and safety.
When selecting appropriate wood screws, consider factors such as material, thread design, and head shape to ensure optimal performance in various environments. Proper maintenance and care are also key to extending the lifespan of wood screws and maintaining their functionality.
Prince Fastener hope this article provides valuable insights for you when choosing and using wood screws, enabling you to handle various connection needs more proficiently. Thank you for reading. Please comment below if you have any questions or wish to explore the topic further.