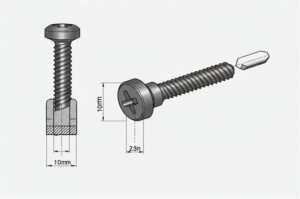
How the bolts and nuts work?
When using bolts and nuts for tightening, the following standards must be followed. There are many thread-tightening operations when assembling machine parts. The tool plays an important role in the tightening work, and the correct tool is used to perform the correct work so that the optimal function of the machine can be achieved and the efficiency of the work can be improved. If you use inappropriate tools or use the wrong method, the work will not only be incorrect and inefficient but also cause injury or damage to products and tools.
There are many kinds of fastening tools, so here are the most commonly used tools, their basic operation, and the basic matters of the construction method of fastening and loosening operations.

1、General fastening work
The general fastening work specified here refers to the use of fastening tools such as wrenches to fasten mechanical parts through bolts, nuts, and washers, etc., without torque limitation, but simply fastening work.
1) Wrench
When using a fixed-caliber wrench, it is important to use a tool compatible with the size of the bolt or nut of the work object because if it is too large, the head of the bolt will be deformed wrench cannot be clamped.
In addition, the length of the wrench is determined by force applied to the wrench, so you should not use methods such as connecting and lengthening the handle, superimposing a greater force with another wrench, etc.
The following figure shows an example of the use of a wrench:
The method of using the wrench shown in Figure 2 is very dangerous.
If the wrench is placed in the position as shown in the solid line and twisted at an acute angle to the AB line of the mechanical part, it will pinch the hand if the catch comes out or if the bolt is broken by too much force. It is safer if the AB line is at an obtuse angle, as shown in the dotted line. In addition, it is better to use the pulling force of the wrench rather than the pressing force. In any case, it is safer to press with the palm of your hand and extend your fingers at the same time when you have to press hard.
This matter can be commonly used for all wrenches, such as double-headed plum wrenches, ratchet handles, pipe wrenches, movable wrenches, and torque wrenches.
2) Sleeve for socket wrench
Sleeves of matching caliber should be used. The casing of metric threads should be used for metric threads, and the casing of unified standard threads should be used for unified agreement threads, which should be classified.
This matter is also suitable for all wrenches of other fixed caliber used for the sleeve of the simple wrench.
2、Tightening work requiring torque control
When the tightening force needs to be controlled, torque wrenches should be used. According to the size and material of bolts and nuts, the tightening force (torque) is determined, and if it is screwed too lightly, it will be loose, and if it is screwed too tightly, it will cause the load to lead to the bolt breaking.
Therefore, it is necessary to use a torque wrench to measure the tightening force at locations where it is important for the function. Torque is generally expressed in N?m. There are several types of torque wrenches, such as the strain type with a display board and pointer to show this index, the dial indicator type, or the preset torque type.
The bolt or nut is temporarily screwed on using a wrench, and then, using a torque wrench, it is formally tightened, and the torque is measured.
What must be noted in measuring the torque is that the casing that meets the size of the bolt or nut is mounted on the torque wrench for use, and the handle must be held, and the force applied when measuring.

3、Prevent the bolt and nut from loosening
In the mechanical part with vibration, measures must be taken to prevent loosening of the case, the bolt, nut anti-loosening treatment. In the anti-loosening treatment, – generally take the following methods.
1) The installation of the washer, see the figure below:
2) Installation of cotter pins
The general matters of cotter pins are as follows.
The shape of the cotter pin should be confirmed to be in accordance with the drawing.
After confirming that the nut is tightened according to the standard torque, install the cotter pin according to the following points.
Confirm that the cotter pin is inserted in the correct direction and that the bolt has an open-end pinhole.
Screw on the slotted nut, insert the cotter pin into the bolt hole, tap it into the pin with a steel chisel, and then pry it off with your hand or a hammer.
When reassembling after disassembly, sometimes the holes may not match up, so use a steel file to slightly file away the inside of the nut and then align it with the next spiral slot. The installation diagram is shown below:
3) Installation of anti-rotation wire
As shown in the diagram, anti-rotation steel wire in the number of bolts for an even number is every 2 bolts for a pair of installation, such as an odd number, 2 a pair, the remaining 3 as a group for installation. Generally use wire pliers to install the anti-rotation wire.
4、The use of thread fastening agent
The threaded fastener is applied to the bonded part of the nut or bolt and slowly hardens to prevent the nut or bolt from loosening due to vibration or impact.
It can be applied on the threads, either on the external threads only or on the internal threads only. The steps are as follows:
①.Degreasing and washing: Use good volatile items such as trichloroethylene, acetone, ether, and alkali solution to clean. Degreasing should be as thorough as possible. Do not use gasoline, light oil, kerosene, etc., which are not volatile.
②、Natural drying: Leave the detergent to dry completely.
③.Gluing: Apply the adhesive on one or both sides in the following way to fill the gap between the threads or occlusal surfaces.
●Apply directly from the container nozzle;
● Dipping (in the case of threads, use a tray);
●Application by brush or brush (in the case of occlusion, use a tray);
In addition, do not pour the liquid back into the container when foreign objects are mixed with the metal sheet or when the liquid is poured into the tray for use.
④、Assembly: After applying glue, fasten it according to the original method.
5、Installation of stop nut
As shown in the figure, use 2 nuts, as shown in Figures 1 and 2; after tightening the 2 nuts together, use a wrench to hold the upper nut, and then tighten the lower nut as much as possible. In this way, the gap prone to shaking becomes as shown in Figure 4, and loosening can be prevented. Note: The arrow shows the direction of the force applied.
6、Tongue washer installation
In the tongue washer inserted into the nut or bolt connected between the mechanical parts and tightened, the root of the washer, as shown in the figure bend, can play a role in preventing loosening.
In the operation of bending the root, first with a steel chisel and hand hammer pry up the ear, and then the tip of the steel chisel pressed to the opposite side of the nut or bolt and the right-angle surface of the mechanical part. When using the steel chisel to pry up the ear, pay attention to avoid injury to the root by the steel chisel tip.
7、Fastening operation and precautions
① The contact surface of the bolt and nut must be flat. If the contact surface is not good, it should be a countersink. (If necessary, you can also use flat washers)
② In the specified bolt, nut fastening order, do not get the order wrong. Generally, in the use of multiple bolts to fasten mechanical parts, as shown in the figure, the order of equal fastening does not deviate by the diagonal position.
③In the process of tightening, if you feel the effort, do not operate brutally. The reason is that this may cause damage to the grain teeth or heat glue. In this case, loosen the bolt and nut, check the threads of both sides with a tap or plate, and adjust the bad side to the correct thread.
If both sides are in good condition, apply appropriate lubricant and then tighten them again.