At Prince Fastener, we live and breathe stainless steel washers. For more than three decades, our engineers have watched a humble, coin-shaped disc evolve into the mission-critical “insurance policy” behind every bolted joint on the planet. Whether you are bolting together a seaside wind turbine in the salty spray of the North Sea, sealing the flanges of a pharmaceutical reactor that must never leak, or simply assembling a food-grade conveyor that runs 24/7, the right stainless steel washer is the silent guardian that keeps your design safe, tight, and corrosion-free.
Today, we open our vault of knowledge to give you the definitive guide on stainless steel washers—an article purpose-built for designers, purchasers, and maintenance managers who refuse to compromise on quality.
In the next few minutes you will discover why 304 dominates indoor machinery while 316 becomes non-negotiable within 1 km of any coastline; why 200 HV is perfect for an 8.8-grade bolt but 300 HV is the only responsible choice under 10 MPa of steam pressure; why a laser-marked Nord-Lock wedge washer can survive 50 000 thermal cycles without losing 5 % preload, and why a nanocoated 316L washer can extend seal life three-fold in a hydrogen sulfide column. We will decode global standards from GB/T 97.1 to DIN 125, translate hardness classes into plain English, and hand you a three-step cheat sheet that turns “I think this will work” into “I know this will last.”
Grab a coffee, bookmark this page, and let Prince Fastener—your single-source partner for stainless steel washers—guide you from confusion to confidence. By the time you reach the final paragraph, you will not only know exactly which washer your application demands, but you will also understand why cutting corners on a few pennies today can cost millions in unplanned shutdowns tomorrow. Let’s dive in.
As Prince Fastener, we know stainless steel washers are common fasteners. They primarily disperse pressure from bolts or nuts, prevent damage, improve sealing, or enhance anti-loosening effects. Here’s a detailed overview of stainless steel washers, including their classification, materials, standards, and application scenarios:
Common Materials and Performance
At Prince Fastener, we understand the critical role material plays in stainless steel washers. Here’s a breakdown of common materials and their ideal applications:
| Material | Characteristics & Applicable Scenarios |
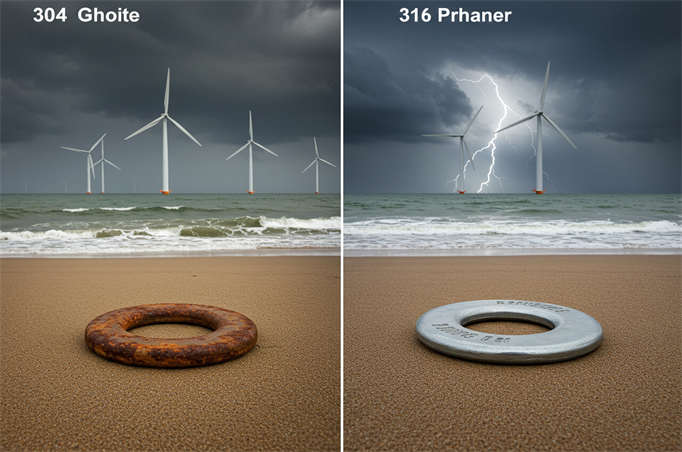
| 304 Stainless Steel | A general-purpose grade with good corrosion resistance, suitable for common indoor and outdoor environments. |
| 316 Stainless Steel (A4) | Contains molybdenum, offering enhanced resistance to salt spray and seawater corrosion. We recommend it for marine or highly corrosive environments. |
| 254 SMO® | A super stainless steel with a PREN value ≥45. We use it for extremely corrosive environments like seawater applications and chemical equipment. |
Common Types and Uses
| Type | Characteristics & Uses |
| Flat Washers | We use them to increase the contact area and reduce indentations, commonly placing them under bolt heads or nuts. |
| Spring Washers | These work with flat washers to prevent loosening and resist vibration. |
| Sealing Washers | Featuring an integrated EPDM or NBR sealing ring, we use them for waterproof and gas-tight applications. |
| High-Strength Washers | With a hardness of ≥300HV, we design these for use with high-strength bolt connections. |
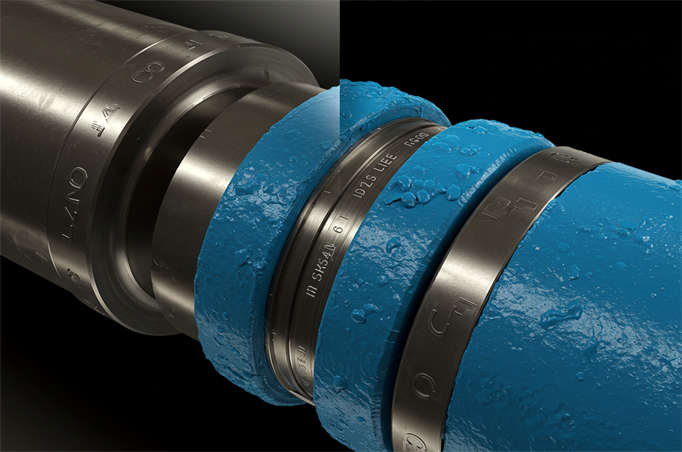
| Anti-Loosening Washers | Like Nord-Lock wedge-locking washers, we use them specifically in vibrating environments to secure fasteners. |
Standards and Dimensions
| Standard Code | Description |
| GB/T 97.1/97.2 | These are Chinese National Standards for Grade A flat washers. We commonly use them for M1.6 to M30 bolts. |
| DIN 125 | This is a German standard often used with hex bolts, with a hardness of ≤250HV. |
| ISO 10673 | This is an International Standard with dimensions similar to GB, making it suitable for export products. |
Selection Recommendations
For general indoor/mechanical assembly, choose 304 material and the GB/T 97.1 standard. For coastal/chemical environments, we recommend 316 or 254 SMO material. If you need waterproofing/dustproofing, select WBAZ-type washers with a sealing gasket. For high-frequency vibration applications, use Nord-Lock anti-loosening washers.
What is the Difference Between 304 Stainless Steel and 316 Stainless Steel?
| Comparison Item | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel (A4) |
| Main Composition | 18% Chromium (Cr) + 8% Nickel (Ni) | 16% Chromium (Cr) + 10% Nickel (Ni) + 2%~3% Molybdenum (Mo) |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Does not contain | Contains Molybdenum, enhancing resistance to chloride corrosion (e.g., seawater, salt spray) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Sufficient for general environments (air, water, weak acids/bases) | Superior, especially resistant to chloride pitting corrosion (e.g., swimming pools, marine environments) |
| Magnetism | Weakly magnetic (may be more noticeable after cold working) | Weakly magnetic (similar to 304) |
| Strength | Tensile strength approximately 520 MPa | Tensile strength approximately 620 MPa (slightly higher) |
| Price | Lower (approximately 60%~70% of 316) | Higher (due to molybdenum and higher nickel content) |
| Typical Uses | Home appliances, cutlery, architectural decoration, general industrial equipment | Medical equipment, chemical equipment, marine vessels, coastal buildings |
The core differences between 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel lie in their chemical composition, corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and usage scenarios. (See Chart 4 for a direct comparison).
304 offers high cost-effectiveness and suits everyday environments. 316 is more expensive but provides stronger corrosion resistance, making it essential for coastal, chemical, and medical applications.
Note: 316L is an ultra-low carbon version of 316 (C≤0.03%). It resists intergranular corrosion after welding, making it more suitable for welded components. If you use 304 in high-salt spray environments (like coastal areas), rust spots may appear. In such cases, you must choose 316 or a higher grade (like 2205 duplex stainless steel).
What are the Uses of Stainless Steel Washers?
The core uses of stainless steel washers are “protection, dispersion, sealing, and anti-loosening.” We can break this down into five specific scenarios:
Protecting Connected Part Surfaces
Stainless steel washers prevent indentations and scratches. When tightening bolts or nuts, the washer transforms point contact into surface contact, preventing the metal surface from “biting” into dents (especially for soft materials like aluminum or plastic). They also isolate electrochemical corrosion; stainless steel washers can separate different metals (e.g., aluminum parts and steel bolts), reducing the potential difference that causes galvanic corrosion.
Dispersing Fastening Pressure
Washers reduce pressure per unit area by increasing the bearing surface. This prevents concentrated bolt pre-load from deforming or cracking the connected part (e.g., during the installation of brittle materials like glass or ceramics). If the connecting surface has slight irregularities, the washer can fill gaps, ensuring uniform stress distribution.
Sealing, Dustproofing, and Waterproofing
For static sealing, washers with rubber sealing layers (like EPDM composite gaskets) prevent liquid or gas leakage, common in pipe flanges, valves, and pump bodies. For dust and moisture protection, ultra-thin stainless steel washers (0.1mm class) seal gaps in precision equipment (e.g., sensors, motor casings).
Anti-Loosening and Vibration Resistance
Spring washers (like DIN127) provide elastic anti-loosening by increasing thread friction through their elasticity, resisting loosening caused by vibration (e.g., in car chassis or machine tools). Mechanical anti-loosening, such as with toothed washers (e.g., Nord-Lock), uses wedge-shaped teeth for self-locking, suitable for high-frequency vibration scenarios (wind power generators, railway vehicles).
Expanding Special Functions
Coated washers (e.g., PTFE-coated) provide insulation and isolation, used for electrical isolation in electronic devices to prevent short circuits. Ultra-thin stainless steel washers (0.05~0.3mm) adjust clearance, precisely setting bearing pre-load or mechanical assembly gaps.
Stainless steel washers are a “multi-functional assistant” for bolted connections: they protect surfaces, disperse pressure, seal media, and prevent loosening. Their corrosion resistance significantly extends equipment life, especially in corrosive environments (e.g., chemical, marine).
What are the Grades of Stainless Steel Washers?
We classify the “grades” of stainless steel washers across four dimensions: material grade, product grade (precision), hardness grade, and standard system. Here’s our systematic breakdown:
I. Material Grade (Stainless Steel Type)
| Material Grade | Characteristics & Uses |
| 304 (SUS304) | This is a general-purpose grade with good corrosion resistance, suitable for most industrial and civil applications. |
| 316 (SUS316) | Containing molybdenum, this grade offers excellent resistance to chloride corrosion. We recommend it for highly corrosive environments like marine, chemical, and medical applications. |
| 316L | This ultra-low carbon version resists intergranular corrosion after welding, making it ideal for welded structural components. |
| 310S / 321 / 630 (17-4PH) | These grades are for special applications requiring high temperature resistance or high strength. We use them less frequently for standard washers. |
II. Product Grade (Precision and Tolerance)
| Grade | Standard Codes | Description |
| Grade A | GB/T 97.1, ISO 10673, DIN 125-A | This is our high-precision grade, perfect for precise assemblies. These washers feature flat surfaces and neatly chamfered edges. |
| Grade C | GB/T 95, DIN 126 | This is our general-purpose grade, suitable for common mechanical assemblies. They offer a lower cost option while still providing reliable performance. |
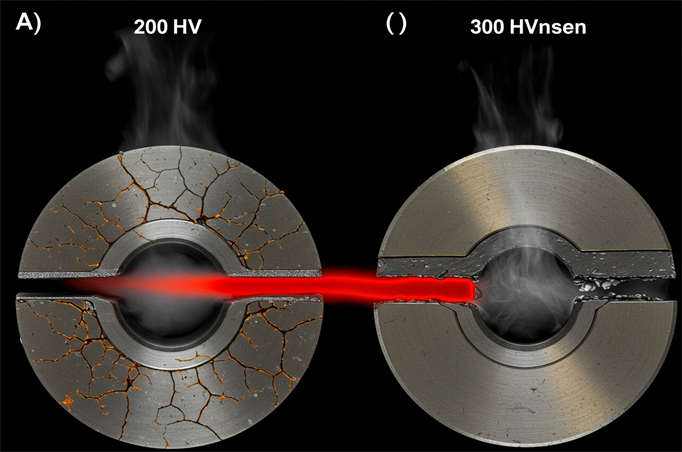
III. Hardness Grade (HV)
| Grade | Hardness Range | Suitable Bolt Grade |
| 200HV | Softer, ideal for low-strength bolts (e.g., A2-70) | N/A |
| 300HV | Medium strength, suitable for Grade 8.8 bolts | Grade 8.8 |
| 400HV | High strength, suitable for Grade 10.9 and above bolts | Grade 10.9+ |
| ≥500HV | Ultra-high strength, used for heavy-duty connections like bridges and wind power | N/A |
IV. Standard System (by Country/Industry)
| Standard System | Common Standard Numbers | Characteristics |
| Chinese National Standard (GB) | GB/T 97.1, GB/T 97.2, GB/T 95 | We classify them into Grade A and Grade C, commonly using metric sizes. |
| German Standard (DIN) | DIN 125-A, DIN 126, DIN 433 | Their dimensions are similar to Chinese National Standards, and we frequently use them for export products. |
| American Standard (ANSI/SAE) | ANSI B18.22.1, SAE | These use imperial sizes and come in Type A/B, which we use with American standard bolts. |
| Japanese Standard (JIS) | JIS B 1256 | We commonly use these in the Japanese market; their dimensions are slightly smaller than DIN. |
| High-Strength Specific | GB/T 97.3 (for clevis pins), JIS B 1186 (for friction connections) | We use these for demanding applications like steel structures and bridges. |
Selection Recommendations
For daily assembly, choose 304 A-grade 200HV GB/T 97.1. For coastal/chemical environments, select 316 A-grade 300HV DIN 125. For high-strength connections, choose 304/316 400HV GB/T 97.3 or JIS B 1186.
How to Choose the Hardness Grade of Stainless Steel Washers?
When selecting the hardness grade (HV) of stainless steel washers, our core principle is to “match it with the bolt’s strength grade, while also considering the usage environment and load requirements.” Here’s our specific selection guide:
1. Match by Bolt Strength Grade
| Bolt Performance Grade | Recommended Washer Hardness (HV) | Description |
| ≤ 6.8 Grade | 100 HV | We use these for light-duty, general structures like wood constructions and home appliances. |
| 8.8 Grade | 200 HV | This is our industrial standard, perfect for machinery, equipment, and vehicles. |
| 10.9 Grade | 300 HV | We recommend these for high-strength connections in applications such as bridges, wind power, and heavy-duty equipment. |
| ≥ 12.9 Grade | ≥ 400 HV (or with hardening treatment) | These are for ultra-high strength applications, often requiring custom or special materials. |
2. Consider Usage Environment
| Scenario | Recommendation |
| High Temperature/High Pressure | We recommend 300 HV and above to prevent crushing and deformation. |
| Coastal/Chemical Environments | We suggest 316 stainless steel with 300 HV for both corrosion and indentation resistance. |
| Vibration/Anti-Loosening Requirements | We pair high-strength washers (300 HV) with an anti-loosening structure for optimal performance. |
| Precision Assembly | We advise choosing Grade A precision with 200/300 HV for stable dimensions. |
3. Practical Selection Slogan
“6.8 matches 100, 8.8 matches 200, 10.9 matches 300, 12.9 adds more.” “For corrosive environments, start with 316; if strength is insufficient, add 300 HV.”
Marking Example
A GB/T 97.1-8-A2-200HV washer indicates an A-grade, 8mm, A2 stainless steel washer with a hardness of 200HV, suitable for an 8.8-grade bolt.
What is the Difference Between Zinc Washers and Stainless Steel Washers?
We can compare zinc washers (usually hot-dip galvanized carbon steel washers) and stainless steel washers across several dimensions: material, corrosion resistance, strength/hardness, cost, and applicable scenarios.
| Comparison Aspect | Zinc Washers (Hot-Dip Galvanized) | Stainless Steel Washers (304/316) |
| Base Material | Low carbon steel (Q195, Q235, etc.) | 304, 316, etc. stainless steel |
| Surface Treatment | Hot-dip galvanized layer (approx. 50-80 µm) | No coating; corrosion resistance from inherent alloy elements |
| Corrosion Resistance | Zinc layer provides sacrificial protection, suitable for neutral outdoor environments; cut edges prone to red rust | Overall corrosion resistance; 316 contains Mo for superior salt spray and chemical media resistance |
| Hardness Grade | Commonly 100-200 HV | Available in 200, 300, 400 HV, and above |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Zinc layer oxidizes and peels easily above 200 °C | Long-term resistance to 500-800 °C; no oxidation or discoloration |
| Cost | Low, approx. 30-50% of the same spec 304 | High, especially 316 |
| Appearance | Silvery-gray zinc spangle, later turns dull/gray | Bright metallic luster, maintains appearance long-term |
| Typical Applications | Building steel structures, photovoltaic brackets, general machinery | Food equipment, marine vessels, coastal areas, chemical, medical |
Selection Recommendations
For budget-priority and general outdoor use, select hot-dip galvanized washers (e.g., GB/T 97 galvanized). For high-corrosion, clean, or high-temperature applications, choose stainless steel washers. Prioritize 316 for coastal or chemical environments.
What Special Uses Do Stainless Steel Washers Have in the Chemical Industry?
In the chemical industry, stainless steel washers offer “all-in-one” functionality. They must resist strong acids, bases, salt spray, and high temperatures, while ensuring zero leakage, zero contamination, and long-term, maintenance-free operation. We summarize their special uses across these six major scenarios:
Reactor and Tower Flange Connections
- Media: Sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, chlor-alkali, ammonia, organic solvents, etc.
- Requirements: Long-term resistance to chemical corrosion, high temperatures (200–500 ℃), and high pressure (1.6–10 MPa).
- Typical Solutions: We use 316L or 254 SMO stainless steel flat washers combined with PTFE-coated or graphite composite gaskets, providing “metal strength + sealing flexibility.”
Sealing for Pumps, Valves, and Heat Exchangers
- Media: Highly corrosive fluids containing chlorides, hydrogen sulfide, organic acids, etc.
- Requirements: Resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking.
- Typical Solutions: We recommend 254 SMO® or Hastelloy C-276 anti-loosening washers, with PREN≥45, showing no rust after 1000 hours of salt spray.
High-Pressure Piping Systems (Steam, Process Gases, Liquefied Hydrocarbons)
- Requirements: Maintain sealing under pressures ≥10 MPa, preventing “blow-outs.”
- Typical Solutions: We utilize 316 stainless steel lens washers or metal ring-type joints (RTJ), with a hardness of 300–400 HV and a surface roughness Ra≤0.8 μm, ensuring line sealing.
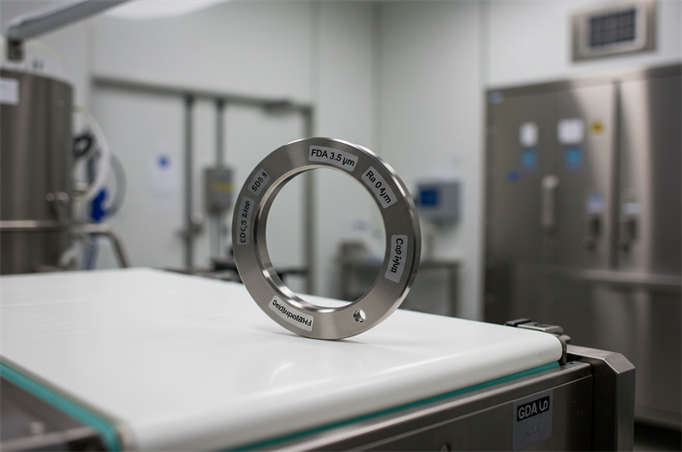
Clean Processes (Pharmaceutical, Food, Fine Chemical)
- Requirements: Surface roughness Ra≤0.4 μm, free of oil and precipitates, compliant with FDA / GMP.
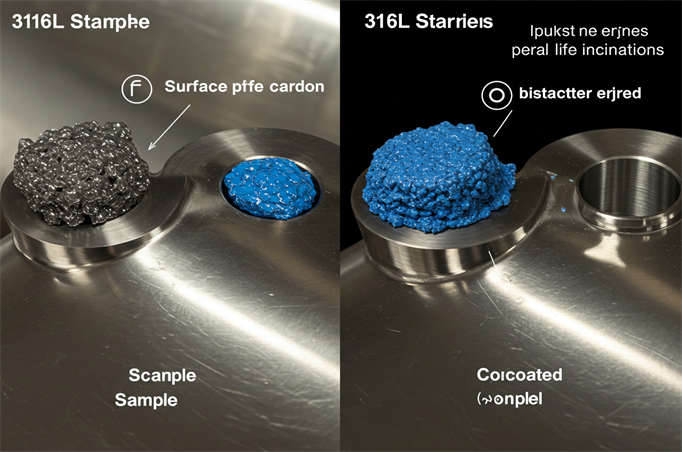
- Typical Solutions: We supply electropolished 316L stainless steel flat washers with nano-coatings (passivation + antibacterial functions), preventing product cross-contamination.
Extreme Temperature/Temperature Difference Conditions
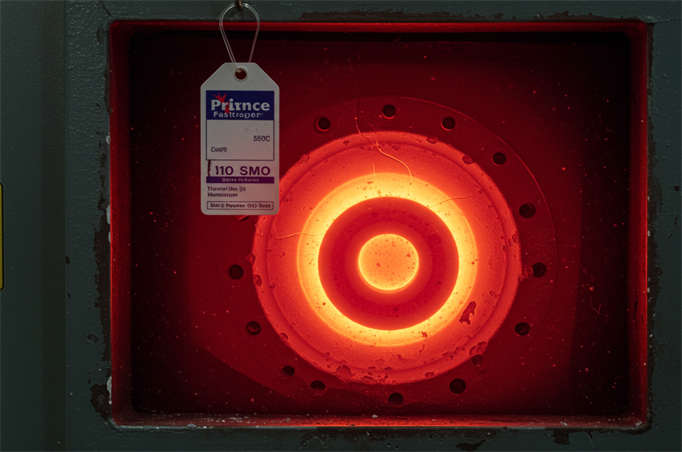
- Scenarios: -196 ℃ liquid oxygen, +550 ℃ cracking furnaces.
- Typical Solutions: We use Inconel 718 or 310S stainless steel washers, maintaining over 80% high-temperature strength and no deformation under thermal shock.
Strong Vibration, Thermal Cycling Equipment (Centrifuges, Compressors, Reactor Mixer Shafts)
- Requirements: Anti-loosening, anti-fretting wear.
- Typical Solutions: We provide 316L stainless steel Nord-Lock wedge-locking washers, with pre-load decay less than 5%, showing no loosening after 50,000 thermal cycles.
Additional Technology Trends
- Nano-coated stainless steel washers: In petrochemical and offshore platforms, coatings can enhance sealing performance by 2 times and extend lifespan by 2–3 times, while also reducing installation torque by 15%.
- Digital traceability: Chemical projects now adopt 316L washers with laser marking and QR codes, enabling full lifecycle traceability of batch, material, and test reports.
Selection Slogan for Chemical Industry
“For strong acids and bases, choose 316L; for chloride-rich and high temperatures, use 254 SMO; for clean medical applications, electropolish and nano-coat; for high pressure, high temperature, use alloy steel.”
How to Choose the Right Washer Material and Type for My Equipment?
To help you accurately select the right washer material and type for your equipment, we guide you through a systematic assessment using five dimensions:
I. Clarify Your Purpose
| Purpose | Recommended Washer Type | Examples |
| Prevent Loosening | Spring washers, conical washers | Vibrating environments like motors and pumps |
| Increase Contact Area | Flat washers | Plastic casings, aluminum components |
| Seal and Waterproof | Rubber washers, PTFE washers | Water pumps, pipe joints, food equipment |
| Prevent Galvanic Corrosion | Washer made of the same material as the base | Copper washers for copper parts, aluminum washers for aluminum parts |
| High-Temperature/Chemical Environments | Stainless steel, PTFE, FKM | Chemical equipment, boilers, HVAC systems |
II. Select Structure Based on Load Type
| Load Type | Recommended Structure | Considerations |
| Axial Load | Flat washers, conical washers | We consider the washer’s resistance to compression and deformation. |
| Dynamic/Vibration | Spring washers, wave washers | We advise against using plastic or ceramic materials for these applications. |
| Shear Load | Metal flat washers | We pair these with high-strength bolts for proper performance. |
III. Select Material Based on Environment
| Environment Condition | Recommended Material | Performance Characteristics |
| High Temperature (>200°C) | Stainless steel, ceramic, FKM | These materials offer strong temperature resistance and resist deformation. |
| Chemical Corrosion | PTFE, fluororubber, stainless steel | These provide excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents. |
| Outdoor/UV Exposure | EPDM, silicone | We choose these for their good weather resistance and slow aging. |
| Food/Medical Applications | Silicone, food-grade PTFE | These materials are non-toxic, easy to clean, and comply with FDA certifications. |
| Electrical Insulation | Plastic, ceramic, silicone | These are non-conductive and offer excellent insulation properties. |
IV. Size Matching Principles
The inner diameter must be greater than or equal to the bolt thread or rod diameter. The outer diameter must be greater than or equal to the screw head diameter (for soft materials, we recommend a slightly larger size). Choose the thickness based on the clamping force requirement; for dynamic loads, we recommend a thicker washer.
V. Recommended Combinations for Typical Scenarios
| Equipment Type | Recommended Combination | Explanation |
| Car Engine | Stainless steel flat washer + spring washer | These provide anti-loosening properties and high-temperature resistance. |
| Food Processing Equipment | Silicone sealing washer | We use these for their waterproof, non-toxic, and easy-to-clean properties. |
| Outdoor Air Conditioner Unit | EPDM flat washer | These offer excellent weather resistance and UV protection. |
| Chemical Pump Flange | PTFE-coated rubber washer | We recommend these for their superior corrosion resistance and sealing capabilities. |
| Electronic Device Casing | EMI fluoro-silicone rubber washer | These provide electromagnetic interference shielding and high-temperature resistance. |
Three-Step Quick Selection Method
- Determine the purpose: Anti-loosening? Sealing? Insulation?
- Assess the environment: Temperature? Corrosive? Outdoor?
- Consider the material: Metal/rubber/plastic/ceramic; match it to the base material to prevent electrochemical corrosion.
If you can provide your equipment type, usage environment (temperature/media/outdoor exposure), and whether you need sealing or anti-loosening, we can directly recommend specific washer models and materials for you.
As you close this tab, remember: every bolted joint is a promise—to your customer, to your crew, to the environment—that nothing will loosen, leak, or corrode on your watch. At Prince Fastener, we keep that promise by shipping more than 120 million stainless steel washers a year, each one laser-inspected for dimension, hardness, and surface finish. From 0.3 mm-thin shims that adjust the preload of a surgical robot to 254 SMO ring-joint gaskets rated for 550 °C Claus reactors, our inventory is engineered to turn the theoretical tables you just read into nuts-and-bolts reality—today, not twelve weeks from now.
Need a custom 316L washer with electropolished Ra 0.4 μm finish, PTFE coating on one side, and a traceable QR code for your next FDA-audited line? We stock blanks, run same-day CNC finishing, and ship with full EN 10204 3.1 certificates. Struggling to decide between 200 HV and 300 HV for a coastal desalination skid? Our metallurgists will model chloride exposure, predict service life, and email you a signed report before the close of business. That is the Prince Fastener difference: stainless steel washers treated not as commodities, but as precision components worthy of the same rigor you give to pumps, valves, and pressure vessels.
So bookmark this guide, share it with your team, and when specification turns into purchase order, reach out via live chat, email, or phone. Tell us the bolt size, the medium, the temperature, the vibration spectrum—then watch us recommend the exact stainless steel washer that will outlast your equipment. Thank you for investing the time to become an informed buyer; we look forward to earning your trust one washer at a time. Prince Fastener—where stainless steel washers stop being an afterthought and start becoming your competitive edge.