When you pick a hex head cap screw for your project, you must think about the newest rules and what your job needs. The main types for 2025 are carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, titanium, and brass screws. You will see grades like MS90725, ASTM A354 BD, and ISO 8.8 or 10.9. Each grade has its own strength and use.
| Specification / Grade | Material & Strength | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| MS90725 / MS90726 | Grade 5 carbon steel, cadmium-plated, coarse/fine threads | Structural and chassis assemblies |
| MS35307 / MS35308 | 300‑series stainless, corrosion-resistant; coarse/fine thread | Naval platforms, moisture zones |
| ASTM A354 BD / ASTM A490M | Alloy steel Grade BD; proof 830 MPa; tensile up to 1,200 MPa | Heavy-duty structural joints |
| Titanium & Nickel Alloy Hex Caps | Weight‑reduced, high strength-to-weight, non-magnetic | Aerospace structures |
| Standard ISO/ANSI Hex Caps | Class 8.8, 10.9 metric grades per ISO 4014/4017 | General industrial hardware |
You should look at five main things: material, standards, size, thread type, and tensile strength markings. The table below shows why material and strength grade are important:
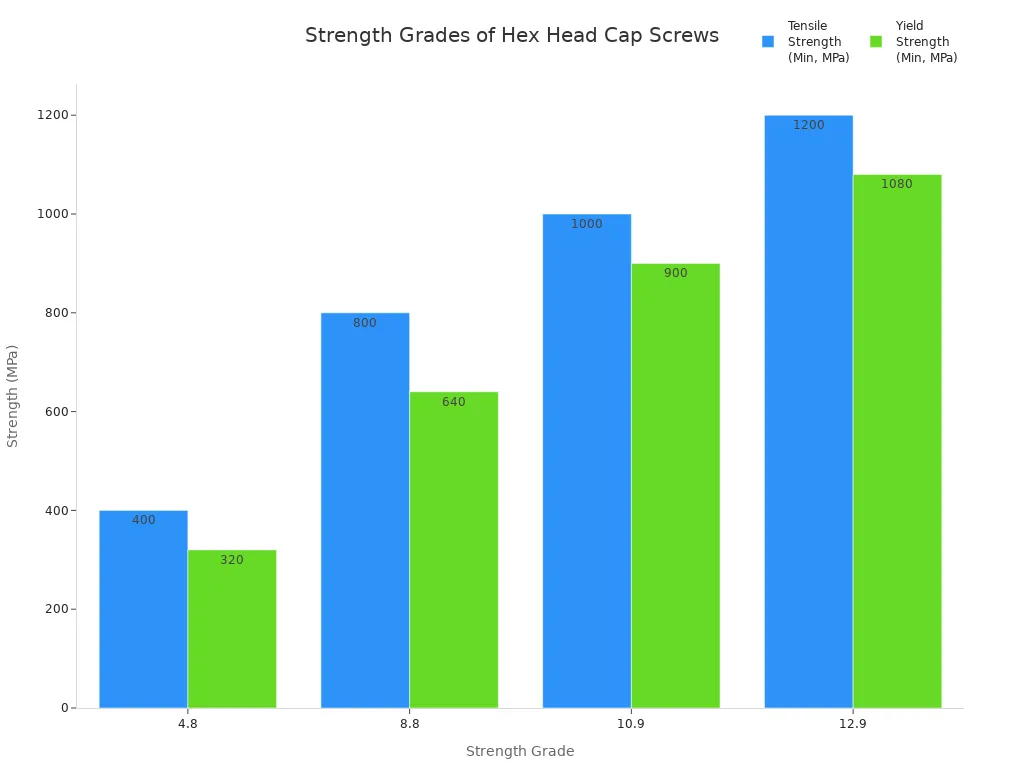
| Strength Grade | Tensile Strength (Min, MPa) | Yield Strength (Min, MPa) | Cenários de aplicação |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 | 400 | 320 | Light structural connections |
| 8.8 | 800 | 640 | Medium-load machinery |
| 10.9 | 1000 | 900 | Maquinário pesado |
| 12.9 | 1200 | 1080 | High-stress, high-precision needs |
Tip: Look at the head markings and grade numbers on the screws. These help you pick the right screw for your job fast and safely.
Principais conclusões
- Escolha o best material for your hex head cap screws. You can choose carbon steel, stainless steel, or titanium. Each one works well for different jobs.
- Learn about the strength grades of screws. Higher grades like 10.9 and 12.9 are stronger. These are good for tough jobs.
- Look at screw sizes and thread types. Metric and inch sizes are not the same. Make sure the screw fits your project.
- Use tables to compare screw types and sizes. This makes it easy to find the right screw for your job.
- Always look at the markings on screws. These show the strength and material. This helps you pick safe and strong fasteners.
Hex Head Cap Screw Types
There are many hex head cap screw types. Each type works best for a certain job. Every type has special features. Knowing these types helps you choose the right screw. Here are the main types used today.
Standard Types
Standard hex head cap screws are used the most. They have a hexagonal head and a washer face. The washer face spreads the load and protects surfaces. These screws come in grades like ASTM A449, SAE J429 Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8. The grade tells you how strong and good the screw is.
| Característica | Hex Head Cap Screws | parafusos sextavados |
|---|---|---|
| Washer Face | Have a washer face under their heads | Do not have a washer face |
| Bearing Surface | Maximum measurement of total bearing surface | Diameter must be perpendicular to the axis |
| Tolerance & Body Diameter | Tighter tolerances across sizes | Looser tolerances |
| Material & Grade | Comply with ASTM A449, A354, SAE J429 | Comply with ASTM A307 Grade A |
You can find standard hex head cap screws in many places: * Cars and buildings * Heavy equipment frames * Building parts * Marine, refinery, and power jobs
These screws are made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. They come in many sizes to fit your needs. Standard types are strong and work well for most jobs.
Note: Always check the grade and markings on your screws. This makes sure you use safe and strong hex head cap screws.
Flanged Types
Flanged hex head cap screws have a wide flange under the head. The flange spreads the load over a bigger area. It also helps stop the screw from coming loose when things shake.
| Recurso | Hex Head Cap Screws | Hex Flange Bolts |
|---|---|---|
| Formato da cabeça | Hexagonal head for easy installation and removal | Flange beneath the head for load distribution |
| Distribuição de carga | Standard load distribution | Enhanced load distribution due to flange |
| Resistance to Loosening | Standard resistance | Improved resistance under vibration |
| Aplicativos comuns | Structural joints, heavy-load components | Automotive engines, heavy machinery, construção |
| Resistência do material | High-strength materials for tensile and shear forces | Similar high-strength materials |
Flanged types are used where you need extra grip. They help keep screws tight even when things move or shake. These screws are used in: | Industry | Application Description | |—————|——————————————————| | Construction | Holding big parts and machines. | | Manufacturing | Putting together machines and equipment. | | Automotive | Holding car and engine parts. | | Aerospace | Making sure planes and spacecraft stay together.|
Flanged types give better load control and keep fasteners tight.
Heavy Types
Heavy hex head cap screws have a bigger, thicker head. You use these when you need more strength. The big head spreads the force out more. This helps stop the screw from breaking under heavy loads.
- The big head spreads force evenly.
- These screws are made for tough jobs and last longer.
- Heavy types meet strict rules like ASTM A193 and A490.
- You can tighten these screws more, which helps in places with lots of shaking.
Heavy hex head cap screws are used in important jobs like bridges, power plants, and big machines. They come in grades like SAE J429 Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8. Each grade gives a different level of strength.
| Padrão | Descrição |
|---|---|
| ASTM A320 Grade L7 | Hex cap screws for low-temperature service. |
| SAE J429 Grade 2 | Low carbon steel screws for general use. |
| SAE J429 Grade 5 | Medium carbon steel, heat-treated for strength. |
| SAE J429 Grade 8 | High-strength fasteners, medium carbon alloy steel. |
Use heavy types when you need the strongest fasteners.
Specialty Types
Specialty hex head cap screws are made for special jobs. There are many kinds, such as:
- Parafusos de segurança: These stop people from messing with them. They have special heads like torx, hex pin, tri-wing, or spanner.
- Parafusos de cabeça cilíndrica: These have a round head with a hex socket. You use them in small spaces and for machines that need to be exact.
- Lag screws: These are good for wood. They have big threads and a hex head for better grip.
- Combi screws: These work with many tools because they have different drive types.
Specialty types are used in oil and gas, energy, and aerospace. You need these screws for high pressure, rust, or very hot or cold places. Hexagon head screws and other special fasteners help with hard engineering problems.
| Atributo | Valor |
|---|---|
| Material | Nylon 6/6 |
| Distance Across Flats | 5.5 mm / 0.217 in |
| Altura da cabeça | 2.6 mm / 0.102 in |
| Tamanho da rosca | M3.5 x 0.6 |
| Comprimento da rosca | 35.0 mm / 1.378 in |
| Pitch/TPI | 0.6 mm |
You can get specialty types in many sizes and materials. This helps you find the right screw for any job.
Tip: Always match the hex head cap screw type to your job. This gives you the best quality and keeps your project safe.
Hex Head Cap Screw Sizes
Escolhendo o right sizes for your screws is important for any project. You need to know the difference between metric and inch sizes. Each type has its own standards and markings. Understanding these details helps you pick the best hex head cap screw for your job.
Metric Sizes
Metric sizes are common in many industries around the world. You will see them in machines, cars, and electronics. The most popular metric sizes include M4, M6, M8, M10, and M12. The “M” stands for millimeters, which tells you the diameter of the screw.
You should also look at the property class markings on metric hex head cap screws. These markings show how strong the screws are. The higher the number, the stronger the screw. Here is a table that shows the most common property classes and their minimum tensile strength:
| Property Class | Minimum Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 8.8 | 800 (≤ 16mm), 830 (> 16mm) |
| 10.9 | 1040 |
| 12.9 | 1220 |
Tip: Always check the property class on the head of the screw. This helps you make sure the screw can handle the load in your project.
You will find metric screws in many lengths and thread pitches. These sizes help you match the screw to the thickness of your materials.
Inch Sizes
In North America, inch sizes are very common. You will see these screws in construction, automotive, and heavy equipment. Inch sizes use fractions to show the diameter. The most popular sizes are 1/4”, 5/16”, 3/8”, and 1/2”. Larger sizes like 5/8” and 3/4” are used for heavy-duty jobs.
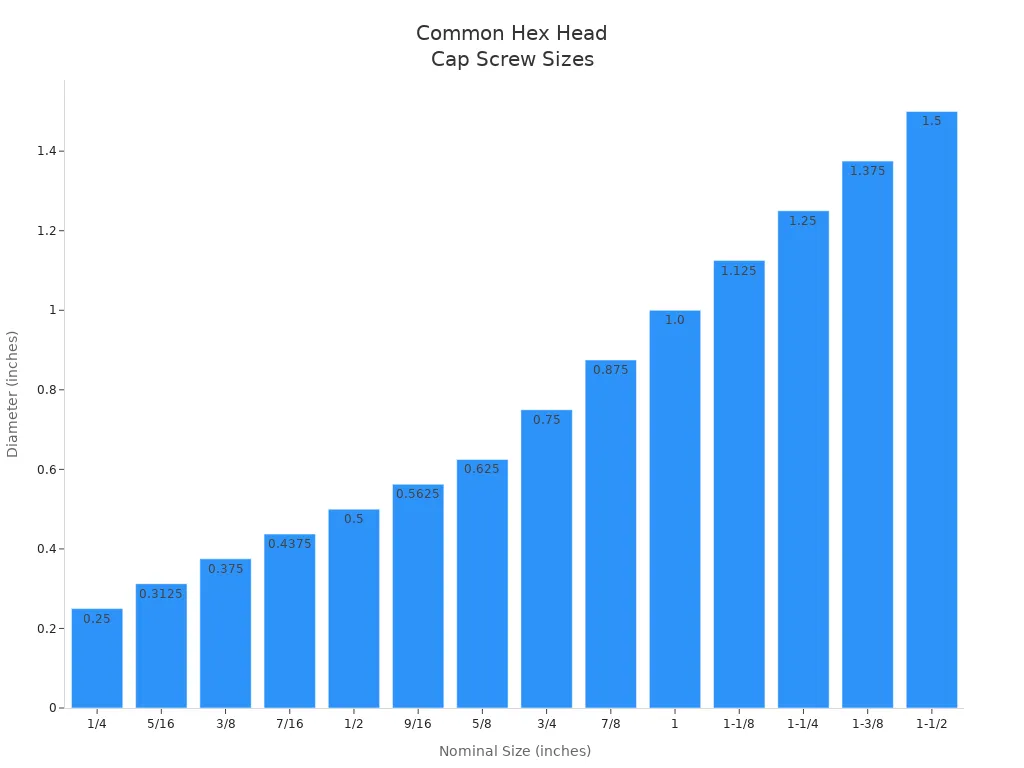
Here is a table of common inch sizes and their diameters:
| Size (inches) | Diâmetro (polegadas) |
|---|---|
| 1/4 | 0.2500 |
| 5/16 | 0.3125 |
| 3/8 | 0.3750 |
| 7/16 | 0.4375 |
| 1/2 | 0.5000 |
| 9/16 | 0.5625 |
| 5/8 | 0.6250 |
| 3/4 | 0.7500 |
| 7/8 | 0.8750 |
| 1 | 1.0000 |
| 1-1/8 | 1.1250 |
| 1-1/4 | 1.2500 |
| 1-3/8 | 1.3750 |
| 1-1/2 | 1.5000 |
You will notice that inch and metric screws follow different standards. Inch screws use ANSI/ASME B18.2.1, while metric screws use ISO 4014 or ISO 4017. Inch fasteners usually have one main standard for size, but metric fasteners can have several. This can change the width across the flats of the screw head.
Length and Thread Pitch
You must also pay attention to the length and thread pitch of your screws. Length tells you how deep the screw will go into your material. Thread pitch is the distance between threads. It affects how tightly the screw holds.
- Thread pitch is important for making sure your screws stay tight.
- It affects how much holding power the screw has.
- You need to match the thread pitch with the nut to stop the screw from coming loose.
- Standard threads work well for heavy-duty jobs.
- Fine threads help stop screws from loosening when there is vibration.
Note: Always check both the length and thread pitch before you choose your screw. This helps you avoid problems with fit and strength.
You will find that hex head cap screws come in many sizes, lengths, and thread pitches. This lets you pick the best screw for your project, whether you need strength, resistance to vibration, or a perfect fit.
Selection Guide
Recomendações de aplicativos
Quando você pick a hex head cap screw, make sure it fits your project. Different jobs need different screws. In cars, you should think about how much weight the screw will hold. You also need to check if the screw works with the materials you use. Each screw has a job in the assembly.
For building things, you want screws that are strong and last a long time. The table below shows two good choices:
| Nota | Descrição | Material | Resistência à tracção | Força de Rendimento | Tratamento térmico |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade-5 | Medium carbon steel, heat-treated | Aço de médio carbono | 120,000 psi min | 92,000 psi min | Oil/water quenched, tempered at 800°F min |
| Grade-8 | Medium carbon alloy steel, heat-treated | Medium carbon alloy | 150,000 psi min | 130,000 psi min | Oil-quenched, tempered at 800°F min |
Electronics need screws that fit well and do not rust. You should look at the thread size and pitch. Make sure the screw matches the material. Always check if the screws follow the right rules. Standards like ISO and SAE help you get safe screws.
Tip: Using the right screw helps your project work well. Always check if the supplier gives good quality and service before you buy.
Material e acabamento
O material and finish of your screws change how strong they are and how long they last. Here are some common choices:
- Steel: Strong and not expensive for most jobs.
- 304 Stainless Steel: Does not rust easily and lasts long. Good for food and tough products.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Best for places with saltwater or strong chemicals.
- Alloy Steel: Very strong for heavy things.
- Nylon: Used for light jobs or when you need non-magnetic screws.
You can pick from many coatings. Hot-dip galvanizing works well outside. Passivation is good for food or medical use. Zinc-aluminum flake and Dacromet coatings stop rust and last up to 1,000 hours in salt spray tests.
| Tipo de revestimento | Effectiveness Description |
|---|---|
| Galvanização por imersão a quente | Stops rust in tough places, good for outside. |
| Passivação | Makes stainless steel better against rust, keeps size the same. |
| Zinc-Aluminum Flake | Lasts up to 1,000 hours in salt spray, very strong. |
| Dacromet Coatings | Lasts longer than other coatings in salt spray tests. |
Always check the standards and thread type for your screws. This helps you avoid problems with fit and strength. If you need self-drilling hex screws or internal hex screws, ask your supplier about quality. Good service helps you find the best screws for your job. High-quality hex head cap screws and self-drilling hex screws give you more ways to use hex head screws in your projects.
Reference Table
Types vs. Sizes Comparison
When you choose hex head cap screws, you need to compare types and sizes to find the best fit for your project. You can use tables to see the differences quickly. Tables help you match the screw type to the size you need.
Here is a table that shows common screw types and their size options. You can see how each type fits different jobs:
| Tipo de parafuso | Common Sizes | Especificações |
|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Cap Screws | M5, M6, M8, M10, M12 | Load, Material |
| Parafusos de cabeça cilíndrica | M3, M4, M5, M6 | Load, Material |
| Phillips Pan Head Screws | #4, #6, #8 | Load, Material |
| Parafusos de cabeça chata | #6, #8, #10 | Load, Material |
You can also look at the size details for metric screws. This helps you check the diameter, width across flats, and head height. These numbers show how the screw will fit in your assembly.
| Nominal Diameter and Thread Pitch | Width Across Flats (mm) | Head Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| M5 x 0.8 | 7.78 – 8.00 | 3.35 – 3.65 |
| M6 x 1 | 9.78 – 10.00 | 3.85 – 4.15 |
| M8 x 1.25 | 12.73 – 13.00 | 5.10 – 5.50 |
| M10 x 1.5 | 15.73 – 16.00 | 6.17 – 6.63 |
| M12 x 1.75 | 17.73 – 18.00 | 7.24 – 7.76 |
Tip: Use these tables to compare screw types and sizes before you start your project. This makes it easier to pick the right screw and avoid mistakes.
You can see that each screw type has its own size range. Some screws work better for small electronics, while others fit heavy machinery. You should always check the specifications for your application. Tables like these help you make fast and smart choices.
You can use the selection guide and table to pick the right hex head cap screw for your project. The table below shows that hex head cap screws are strong and good for holding things together:
| Type of Cap Screw | Características | Formulários |
|---|---|---|
| Parafuso de cabeça sextavada | Hexagonal shape, heavy-duty | Good for big jobs and keeping things tight |
Here are some tips when you pick high-quality hex head cap screws:
- Choose the right material for your job and where you use it.
- Look at the standards and how strong the screw is.
- Use the right coating and make sure the screw lines up to stop thread problems and breaking.
Quality is very important for safety and making sure things work well.
Perguntas frequentes
What do the numbers on hex head cap screws mean?
You see numbers like 8.8 or 10.9 on the screw head. These numbers show the strength of the screw. Higher numbers mean the screw can hold more weight and handle more force.
How do you choose the right size for your project?
You measure the diameter and length of the screw. Match these to the thickness of your materials. Use tables to check which size fits best for your job.
Can you use stainless steel screws outdoors?
Yes, you can use parafusos de aço inoxidável outside. Stainless steel resists rust and lasts longer in wet or salty places. You should pick 304 or 316 stainless steel for the best results.
What is the difference between coarse and fine threads?
Coarse threads have bigger gaps between each thread. Fine threads have smaller gaps. You use coarse threads for quick assembly. Fine threads work better when you need extra grip or vibration resistance.
Why do some screws have a flange under the head?
A flange spreads the load over a bigger area. This helps keep the screw tight and stops it from loosening when things shake. You see flanged screws in cars and machines.