You use threads and fasteners when you build or fix things. You also use them when you upgrade something. The main types you should know are bolts, screws, nuts, and washers. If you pick the right kind, you save time and money. The correct fasteners can make installation up to 60% faster. Many projects fail because of fastener mistakes:
- 95% of fastener failures happen during installation or fixing.
- 5% of failures happen when you choose the wrong fastener.
Knowing how to choose the right threads and fasteners helps you avoid these mistakes.
要点
- Know the main types of fasteners. These are bolts, screws, nuts, and washers. Picking the right one saves time. It also stops your project from failing.
- Learn how metric and imperial threads are different. Always check which system your project needs. This helps you avoid breaking parts.
- Use tools like thread pitch gauges and calipers. These tools help you find the right fasteners. Good measurements stop mistakes. They also make sure connections are strong.
- Pick fasteners that match the material and environment. This stops rust and keeps things lasting longer.
- Use a checklist when picking fasteners. Check the size, strength, and how easy it is to install. This helps you avoid common mistakes.
Types of Threads and Fasteners
Knowing about threads and fasteners helps you make strong connections. You should learn the basics like what a thread is. Thread pitch means how far apart the threads are. Thread fit tells you how well parts match. These things help you choose the right fastener and avoid problems.
Metric vs. Imperial
There are two main ways to measure threads. One is metric and the other is imperial. Each uses different units and rules. The table below shows how they are different:
| アスペクト | Metric Threads | Imperial Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Units | Measured in millimeters | Measured in inches |
| Thread Form & Angle | Standardized 60-degree angle | Various angles, commonly 60 or 55 degrees |
| Tolerance & Fit | Adheres to ISO standards | Follows Unified Thread Standard, differing tolerances |
| Strength & Precision | Finer pitch for higher precision | Variable pitch for flexibility |
Metric threads are used a lot in Europe and Asia. They are more exact and parts fit together better. Imperial threads are common in the United States and Canada. They give you more choices but do not always match metric parts.
ヒント: Always check which system your project needs before buying fasteners. Mixing metric and imperial can break parts or make weak connections.
Metric threads use millimeters to measure the space between threads. Imperial threads use threads per inch (TPI). This changes how you match nuts and bolts. If you use the wrong type, the threads can get ruined or the fastener can break.
Thread Profiles
Thread profiles show the shape and angle of the threads. Each profile has its own job and good points. Here is a table of common thread profiles and where you use them:
| Thread Profile | 特徴 | 代表的なアプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| V-Thread | Triangular cross-section, 60° or 55° angle | General-purpose fastening |
| Square Thread | Straight and parallel flanks, low friction, high load capacity | Specialized machinery |
| Buttress Thread | Asymmetric trapezoidal shape, strong in one direction | Hydraulic presses, jacks |
| Round Thread | Rounded profile, low-stress concentration | Light bulbs, bottle caps |
| Trapezoidal Thread | Trapezoidal profile, good for power transmission | Lead screws in machines |
Most bolts and screws use V-threads because they hold tight and work for many jobs. Square and trapezoidal threads are used less but are good for heavy loads or special uses. When you look at a thread chart, you can see the shapes and sizes for each profile.
注記: Thread pitch is the space between threads. It affects how tight the fastener holds. Finer threads are more exact but can be weaker. Coarse threads are stronger and do not strip as easily.
Thread Identification
You need to know what threads and fasteners you have before you replace or match them. This step stops mistakes and saves time. Here are some tools and ways to help you:
- Thread Pitch Gauge: This tool has blades that match the screw thread. You use it to find the right pitch.
- Calipers: Calipers measure the width of bolt threads or nuts. This helps you pick the right size.
- Nut/Bolt Gauge: This tool lets you check your fastener against known sizes quickly.
- Ruler or Measuring Tape: If you do not have special tools, count the threads in one inch or measure the space between threads in millimeters.
ヒント: Clean the threads before you measure. Dirt or rust can give you the wrong size.
When you put in a threaded fastener, use the 3-thread rule. Make sure at least three full threads stick out past the nut. This keeps the nut tight and stops it from coming loose. In places with lots of shaking, like cars or machines, use a threadlocker. This glue keeps the fastener from moving.
Common Types of Threads and Fasteners
You will see many kinds of threaded fasteners in home and work projects. Here are the most common:
- Screws: Fasteners with threads on the outside and strong grip.
- Bolts: Fasteners with threads on part of the body that hold two things together.
- Nuts: Fasteners with threads inside that lock bolts in place.
- Rivets: Fasteners that join things together forever.
- Washers: Discs that spread out the force of nuts and bolts.
- Nails: Thin metal pieces for joining wood.
- Anchors: Fasteners for attaching things to concrete.
Some popular screw types are:
- Machine screws: Used for metal-to-metal jobs.
- Deck screws: Used for outdoor wood projects.
- Sheet metal screws: Used for joining metal pieces.
- Drywall screws: Used for putting drywall on studs.
- Hex lag screws: Used for heavy-duty wood jobs.
You will also find wood screws, deck screws, sheet metal screws, and tek screws for special jobs. Each type has its own screw thread and works best in certain materials.
Remember: The weakest part of a bolt is usually at the thread root. Always pick the right thread pitch and profile for your job.
By learning about threads and fasteners, you can choose the best parts for your project. This helps you avoid mistakes and build strong, safe connections.
Fastener Types

Bolts and Screws
Bolts and screws hold things together. Each kind has special features. These features help you pick the best one for your job. Here are some common types:
- ラグスクリュー are thick and have a hex head. You use them for big jobs like decks.
- Set Screws do not have a head. They sit flat and work in furniture or machines.
- Socket Screws have a round head with a hex hole. You use them when you need a lot of turning force.
- Flange Screws have a built-in flange. This spreads out the force and you do not need a washer.
You can see more bolt types and what they do in the table below:
| ボルトタイプ | Distinguishing Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| フランジボルト | Flange under the head spreads load. | Engines, transmissions |
| Plow Bolts | Tapered neck, flat or domed head. | Bulldozers, snowplows |
| Hex Head | Six sides for easy gripping. | General fastening |
| Square Head | Four sides, resists rounding. | Tight spaces, traditional uses |
| Flat Head | Sits flush, countersunk. | Aesthetic jobs |
| Round Head | Dome-shaped, visible after install. | Decorative, light-duty |
| Socket Head | Internal hex drive, high torque. | 高ストレスな仕事 |
| 粗ネジ | Fewer threads per inch, quick install. | Wood, plastic |
| ファイン・スレッド | More threads per inch, strong against vibration. | Precision jobs |
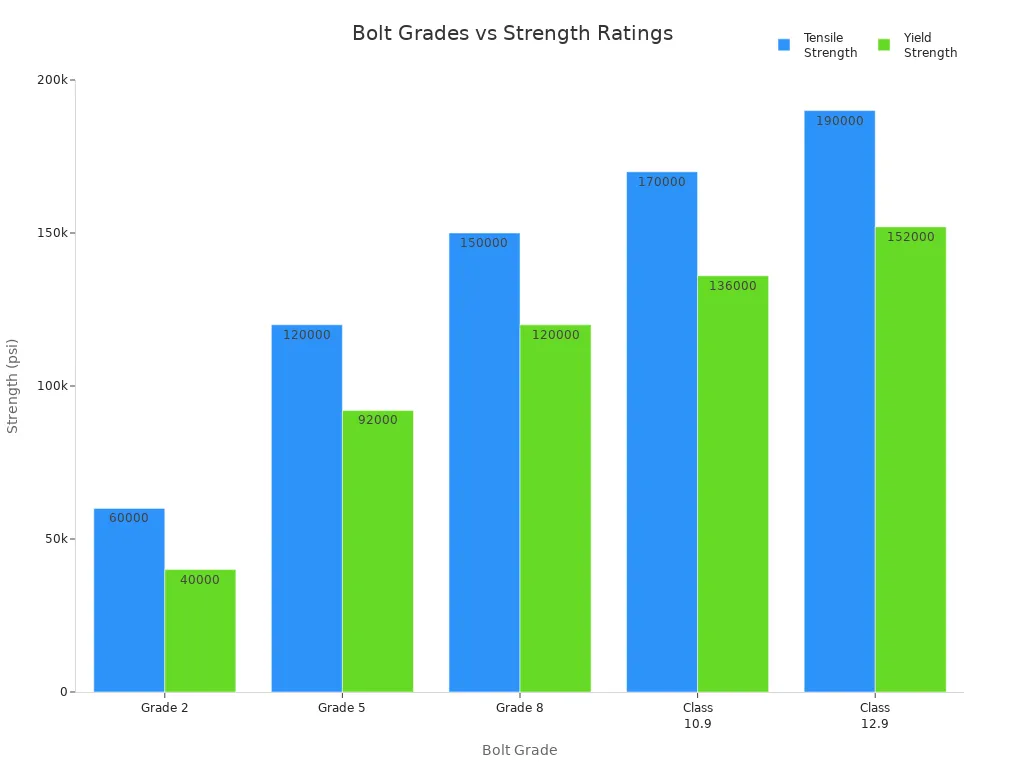
その strength of bolts and screws depends on their grade and material. Stronger grades work better for heavy things. You can see how bolt grades compare in the chart below:
Tip: Always check the screw thread and bolt threads before you put them in. Use a thread chart to find the right type.
Nuts and Washers
Nuts keep bolts in place. Washers protect surfaces and spread out the force. You need both for strong and safe connections. Washers help stop fasteners from coming loose when things shake or get hot and cold. They also keep soft things like wood from getting ruined.
Here is a table that shows how different washers work:
| 洗濯機タイプ | Functionality | Load Distribution Role | Joint Security Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Washers | Spread load, protect surfaces. | Excellent for spreading clamping load. | Minimal, mostly for load distribution. |
| Lock Washers | Prevent loosening from vibration, add spring force. | Distribute weight, lock bolts in place. | Extra security under dynamic conditions. |
Note: Always use the right washer to keep your threaded fastener tight.
特殊ファスナー
Specialty fasteners fix hard problems in many jobs. You find them where regular fasteners do not work. Here are some examples:
| Specialty Fastener Type | Common Industries Used In |
|---|---|
| Socket Head Screws | Machinery, automotive, mechanical equipment |
| High-Tensile Bolts | Construction, mining, heavy machinery |
| ステンレス鋼ネジ | Marine, chemical, food production |
| Titanium Fasteners | Aerospace, high-performance cars |
| Weld Studs | Construction, manufacturing |
Specialty fasteners use strong materials and smart designs. Stainless steel fasteners do not rust and last longer. Some fasteners use recycled stuff to help the planet. Others can handle heat, shaking, or even track loads to warn you about weak spots.
Callout: Specialty fasteners keep machines safe in tough places like near the ocean or in factories. They help you build strong and safe systems.
You need to know about threads and fasteners to pick the right one for your job. This helps you avoid mistakes and build things that last.
Choosing Threads and Fasteners
Picking the right threads and fasteners helps your project last. It also keeps things safe. You should think about what materials you are joining. You need to know how strong the fastener must be. Think about where you will use it. Smart choices stop rust and weak spots. They also help you avoid dangerous problems.
素材適合性
Always match the fastener material to the parts you join. This stops rust and keeps things strong. Here are some things to think about:
- Know what your project needs. Think about how much weight the fastener will hold. Check if it will touch water or chemicals.
- Think about how strong the fastener must be. Ask if it will face pulling or shearing force.
- Make sure the fastener material works with the parts you join. This stops problems like galvanic corrosion.
- Look at where you will use the fastener. If it is outside or near water, pick ones that resist rust. Stainless steel or nickel alloys work well.
- Make sure the fastener can handle heat or cold.
- Think about cost and how well the fastener works.
Pick the right fastener material for your project. Stainless steel is great for places with lots of rust. Zinc-plated or coated fasteners work for easier jobs.
Galvanic corrosion happens when two different metals get wet. One metal rusts faster than the other. For example, steel bolts with aluminum parts can make aluminum rust quickly. To stop this, use fasteners made from the same material as the parts.
Strength and Application
You need strong fasteners for your project. Each fastener has a grade or class. This tells you how much force it can take. The right grade keeps your project safe.
| ボルトグレード | 引張強さ(psi) | Yield Strength (psi) | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| グレード2 | 60,000 | 40,000 | Light-duty applications |
| グレード5 | 120,000 | 92,000 | Automotive and industrial applications |
| グレード8 | 150,000 | 120,000 | Heavy machinery and high-stress applications |
| Class 10.9 | 170,000 | 136,000 | Demanding industrial applications |
| Class 12.9 | 190,000 | 152,000 | Aerospace and ultra-high-stress environments |
- Grade 2 bolts are good for light jobs like furniture.
- Grade 5 bolts work for cars and machines that need more strength.
- Grade 8 bolts are best for heavy equipment and places with lots of stress.
- Class 10.9 and 12.9 bolts are used in tough jobs like factories or airplanes.
Always check the strength before you pick a fastener. If it is too weak, it can break or come loose. If it is too strong for soft parts, it can damage them.
Mistakes to Avoid
People make mistakes when picking threads and fasteners. These mistakes can make your project fail or unsafe. Here are some common problems and ways to avoid them:
- Using the wrong fastener type. Always check what materials and loads you need.
- Using the wrong torque. Use a torque wrench to tighten fasteners just right. Too much force can break it. Too little can let it come loose.
- Mixing different metals. This can cause rust. Try to match the fastener material to the parts.
- Picking the wrong size. Measure the thickness before you choose a fastener.
- Ignoring the environment. Use stainless steel or galvanized fasteners in wet or salty places.
- Forgetting about vibration. Use locking nuts or washers if your project will shake.
- Not installing fasteners right. Make sure everything lines up before you tighten.
Tip: Always check the thread fit and pitch. If you use the wrong screw thread or bolt threads, you can strip the threads or make the connection weak.
Here is a table that shows what can go wrong if you pick the wrong thread fit or pitch:
| Mechanical Failure Type | 説明 |
|---|---|
| Oversized Threads | Fasteners can rattle, seals may leak, or fittings can fail pressure tests. |
| Thread Misalignment | Bolts can strip, torque becomes uneven, and installation gets harder. |
| Tapered or Deformed Threads | Threads do not engage well, which can cause leaks or failures. |
| Thread Pullout | Threads can strip under load, especially in soft materials. |
| Thread Pitch Deviation | Fasteners can jam or turn unevenly, making the assembly weak. |
If you follow these tips and check a thread chart first, you can avoid most problems. Good choices help you build strong and safe projects that last.
Reference Guide
Chart of Threads and Fasteners
When you need to pick the right threaded fastener, a good thread chart helps you make smart choices. You should look for charts that show the most important details. These include the major and minor diameters, pitch, and threads per inch (TPI) for each type of screw thread. The chart should also list common thread standards like Unified National Coarse (UNC), Unified National Fine (UNF), and ISO Metric. This information helps you match bolt threads and nuts, so you avoid mistakes and keep your project strong. Using a thread chart makes it easier to find the right size and type for your job. You can check if your fastener will fit and hold up under stress. This step is key for safety and for making sure your connections last.
ヒント: Always double-check the thread pitch and diameter before you buy or install threaded fasteners. This saves you time and prevents damage.
Selection Checklist
You can use a checklist to make sure you pick the best threaded fastener for your project. Follow these steps to avoid common problems:
| ステップ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Material Compatibility: Choose fasteners made from materials that match the parts you join. This helps prevent rust and keeps things strong. |
| 2 | Environmental Conditions: Think about where you will use the fastener. Will it face water, heat, or chemicals? Pick one that can handle those conditions. |
| 3 | Size and Strength: Make sure the fastener is the right size and strong enough for the load. |
| 4 | Ease of Installation: Pick fasteners that are easy to install or remove. Check if you need special tools. |
| 5 | Cost Efficiency: Choose a fastener that works well and fits your budget. |
Here is a simple checklist you can follow:
- Pick the right material for your threaded fastener and the job.
- Make sure the fastener meets the load and strength needs.
- Balance resistance to rust with the strength you need.
- Choose a trusted fastener brand or supplier.
If you use this checklist and a reliable thread chart, you will find it easier to select the right screw thread or bolt threads for any project. This helps you build safe, strong, and lasting connections every time.
Understanding threaded fasteners, screw thread types, and bolt threads helps you build safe and reliable projects.
- Learn the main types and grades of fasteners for each job.
- Use a thread chart and checklist to match the right threaded fastener to your needs.
Double-check your selections and inspect your work. This simple habit prevents costly mistakes and keeps your connections strong for years to come.
よくあるご質問
What is the difference between a bolt and a screw?
You use bolts with nuts to hold things together. Screws go directly into materials and hold by their threads. Bolts often need washers, while screws do not.
How do I know which thread type to use?
Check your project’s requirements. Look at the size, material, and where you will use it. Use a thread chart to match the right threads and fasteners for your job.
Why do fasteners sometimes loosen over time?
Vibration, temperature changes, or improper installation can cause fasteners to loosen. You can use lock washers or threadlockers to help keep them tight.
Can I mix metric and imperial threads?
No, you should not mix metric and imperial threads and fasteners. Mixing them can damage the threads and make the connection weak or unsafe.
How do I prevent rust on fasteners?
Choose stainless steel or coated fasteners for wet or outdoor areas. Keep fasteners clean and dry when possible. This helps prevent rust and keeps your connections strong.