Fastener Basics: The Essential Guide to Knowing Fasteners
Selecting fasteners can be a worrisome job when there’s a variety of choices laid out for different kinds of applications. It is never a bad idea to ask the important questions that matter to achieve the success of your project, not even searching for the essential information about fasteners.
Today, knowing the basic knowledge of fastening is the best step in overcoming risks and using the components to their full potential. Let’s get to know the useful details about fasteners and their quality in this article.
Benefits of Selecting the Right Fastener
- Reduce risks of safety to workers
- Reduce chances of different application failures
- Highlights fastener life or longevity
- Reduce labor, repair, and maintenance costs
- Avoid higher costs of materials
Common Fastener Types
There are a variety of wood screws that are used in several wood applications or other soft materials. They usually have a combination of large threads and a smooth shank that works perfectly in pulling two materials together.
Have full threading in the body with a bolt-like point tip which needs a nut to successfully affix parts together.
They have a sharp point tip and full large thread that is designed to be driven directly in several materials like plastic, fiberglass, wood, metal sheets, or metal.
Have a distinct head that is socket type with an internal hex socket for a specific drive. They may have longer smooth shanks than threaded lengths.
The most common type of bolt that is used in machinery and construction is the Hex bolt. They are partially threaded in the body and require nuts for securing assemblies.
This bolt has a dome-head with a square section underneath for easy pulling on materials which also prevents spinning of the body during installations. They are typically used in applications that require a smooth surface afterwards like elevator floors.
In definition, nuts are circular metal with internal threading that matches screws or bolts in application to tighten and secure objects together. They also generally help prevent loosening and failures in the assembly.
Washers
This fastener is used along with screws, bolts, and nuts to distribute the load on the surface material and prevent loosening and breakage of the components.
Fastener Materials
Stainless Steel is the most common material for different kinds of fasteners suitable for outdoor and even marine applications. Stainless steel offers a good amount of corrosion resistance, durability, and rust resistance.
Brass and Bronze have almost the same resistance to corrosion as stainless steel properties yet are more expensive. This material is often preferred for its decorative look in applications.
Alloy Steel is a highly hardened material usually coated in black oxide to provide corrosion resistance.
Zinc-plated Steel is composed of low-carbon steel for relatively cheaper costs which provide moderate corrosion resistance. The finish color may vary on the process but are usually in blue-ish tint or yellow.
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel has a thicker layer of coating for better corrosion resistance and is often performed as a final coating on materials of fasteners to suit different environmental conditions.
Chrome and Nickel Plated Steel are other forms of coating on fasteners that offers moderate corrosion resistance, and a smooth or polished appearance.
Fastener Grade/Class
Fastener grade or class refers to the mechanical properties of fastener materials that identify their strength. The manufacturer’s stamp which appears in markings or numbers usually found in the head of bolts. The higher the number indicated the stronger and hardened the material of the fastener.
Common Examples of Fastener Grades:
- Grade 2 (low carbon steel)
- Grade 5 (medium carbon steel)
- Grade 8 (high carbon steel)
- Class 8.8 (medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered)
- Class 10.9 (alloy steel, quenched and tempered)
- Class 12.9 (alloy steel, quenched and tempered)
- A2 & A4 Stainless (Steel alloy with chromium and nickel)
Screw Thread and Terms
Screw Thread is found in the internal and external surface of the cylinder which forms a conical spiral cone or conical helix
- Internal Thread is the inside thread beyond the outer surface
- External Thread is the outer or visible thread on the surface
- Types of Thread
- Fine Thread refers to the large number of threads per distance along the body of fasteners
- Coarse Thread refers to a low number or larger distance of threads along the body of fasteners
Major Diameter is also known as outside diameter which is the largest diameter of the thread of the screw or nut
Minor Diameter also referred to as core diameter or inside diameter contrasts with the smaller diameter of the thread of the screw
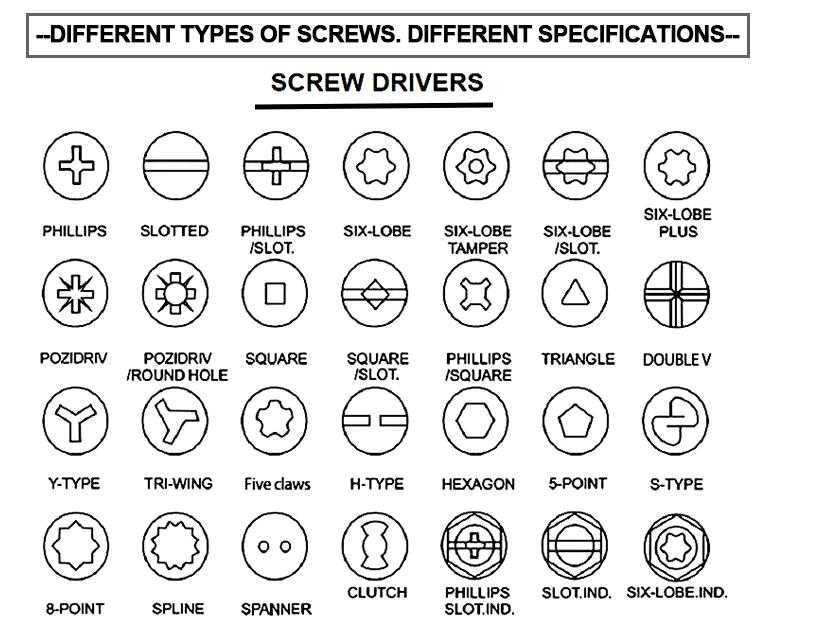
Drive Types
Phillips and Slotted are the most common screw drives that require easy hand tools
Hex sockets (Allen) are common drives for socket screws
Star and Square drives are used for anti-tampering and will not easily cam-out
Fearson and Pozidriv drives are similar to Phillips but less likely to cam-out
Combo drives are available for several fastener types because of their convenience
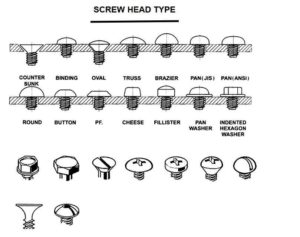
Head Styles
The flat head is a type of countersinking head that is used for flat surface applications
The Pan’s head has a slight dome-head that sits flush on the surface
The hex head is common for large bolts or screws which requires a wrench tool for tightening or removal
Roundheads have larger dome-head shapes compared to pan heads and are primarily used for their decorative finish
The oval head is another type of countersinking head with a low dome under the head
Truss’s head has a slight or medium dome-head that appears wide on the application surface
The button head is typically used with a hex socket drive to provide a slight anti-tampering advantage on screws
Socket heads have a narrow space inside the head with a socket drive and outside knurled sides
In summary, the fundamental guide on fasteners includes knowing their types, materials, grade/class, thread, drive types, and head styles. These features help individuals or organizations who venture into DIY-ing or building products that essentially require the use of fasteners. For critical assemblies on large projects, it is best to consult professional opinions from experts that can support more technical information about fasteners. Know the proper functions and capabilities of different fasteners and related components to ensure the safety and secure use of the devices.
Get professional fastening advice from a leading manufacturer and supplier of industrial fasteners, contact us directly and get a free quotation for high-quality products. We carry a wide range of standard and non-standard fasteners for different kinds of applications.