Choosing the right sheet metal screw sizes depends on how thick the material is. It also depends on what kind of material you use. The way you use the material matters too. Using the correct sheet metal screw sizes helps you:
- Get a strong hold and stop screws from pulling out
- Spread weight evenly to lower the chance of breaking
- Stop screws from stripping by using the right thread
- Make your projects last longer and stay safe
Principales conclusiones
- Elige el tamaño de tornillo correcto for the material’s thickness and type. This helps the screw hold tight and stops damage. Using the right screw size keeps threads from stripping and screws from being loose. This makes your project safer. Always look at a screw size chart before you start. Match the screw’s diameter and length to what you need.
Why Sheet Metal Screw Sizes Matter
Screw Anatomy and Function
When you look at sheet metal screw sizes, you notice that each screw has several important parts. The head, thread, shank, and material all play a role in how the screw works. The head style, such as flat, pan, or round, changes how the screw sits in your project. Flat heads let screws sit flush with the surface, which helps in places where you want a smooth finish. Pan and round heads give extra holding power when you need strength more than looks.
The threads wrap around the screw and help it grip the metal. Strong threads resist pullout forces, so your project stays together. The shank, which is the long part of the screw, affects how much weight the screw can hold. You also need to think about what the screw is made of. Carbon steel is strong but can rust. Titanium is much stronger and works well in tough jobs. When you focus on choosing the right screw, you make sure your project is safe and strong.
Tip: Always match the screw material to your project needs for better holding power and durability.
| Característica | Descripción | Impact on Holding Power |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de cabeza | Flat, pan, round | Changes torque and installation ease |
| Tipo de hilo | Shape and depth of threads | Improves grip and pullout resistance |
| Shank Design | Length and diameter | Boosts load-bearing and shear strength |
| Material | Carbon steel, titanium | Affects strength and corrosion resistance |
Impact of Size on Performance
Sheet metal screw sizes affect how well your project holds together. Larger diameters give more strength and increase the durability of your assembly. For example, a screw with a core diameter of 3.8 mm lasts longer than one with 3.0 mm. Bigger screws also let you use more torque, which means you can tighten them better. The maximum pullout load goes up as the screw diameter increases, so your project can handle more force.
When you focus on choosing the right screw, you avoid problems like stripped threads or loose fits. You also make sure the screw matches the thickness and type of metal you use. If you pick the wrong size, your project may not last as long or stay safe. Always check sheet metal screw sizes before you start your work.
- Sheet metal screw sizes matter for strength, safety, and durability.
- The right size helps you avoid damage and keeps your project secure.
- You get better results when you match screw size to your application.
Key Factors for Choosing Screw Sizes
Material Thickness and Type
You have to pick screw sizes that fit your material. Thin materials often need rivets or nut plates. Thick materials need screws with deeper threads. The right screw length gives a tight grip. It should not poke out the other side. Always check the gauge and thread type first. Here is a simple guide:
| Material Grosor | Recommended Fastening Method |
|---|---|
| Thin Materials | Rivets or nut plates |
| Thick Materials | Screws or bolts with deeper threads |
Tip: Use the right screw size for each material. This helps you avoid weak spots.
You should also look at industry rules for fasteners. These rules help you pick screw length, head style, and thread type.
| Specification Type | Detalles |
|---|---|
| Indicador | 0 to 14 (outer diameter) |
| Material | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel 304/316, Brass |
| Tipo de hilo | Types A, AB, B, Hi-Lo |
| Estándares | DIN 7981, DIN 7982, ISO 7049, ASTM B151 |
Load and Strength Needs
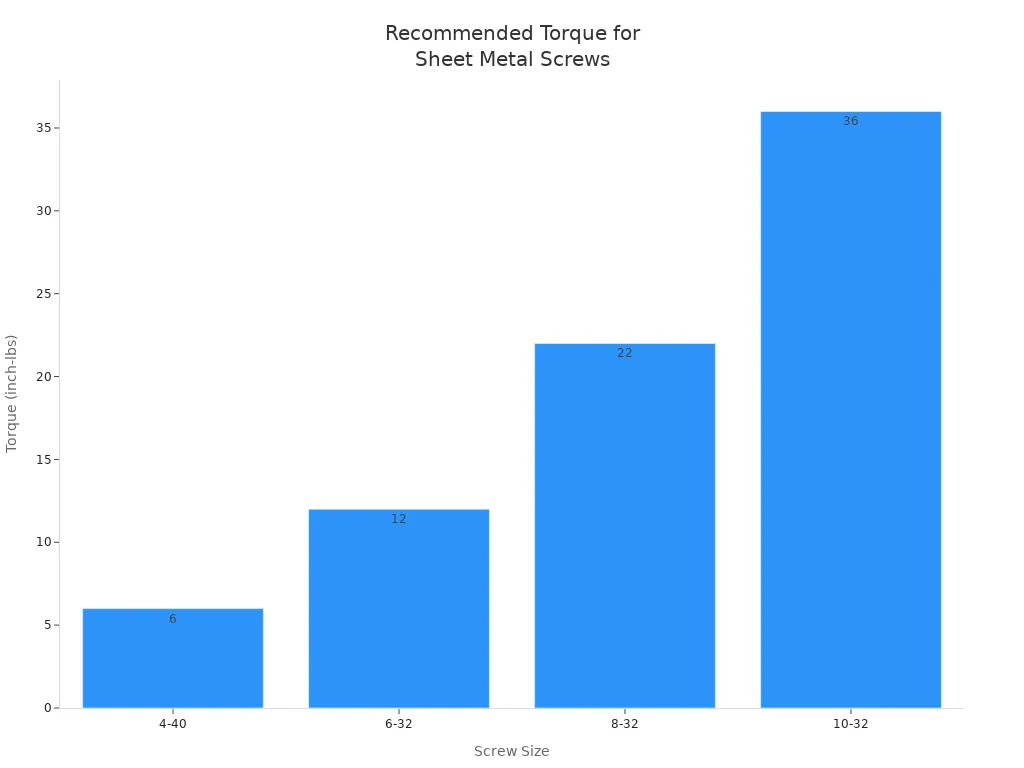
Think about how much weight your screws will hold. Bigger screws and longer screws are stronger. If you use the wrong size, your project might break. Always check the torque for your screw sizes. This chart shows torque values for common screw sizes:
Environmental and Corrosion Factors
Water and chemicals can hurt some fasteners over time. Pick screw sizes and materials that do not rust. Stainless steel and galvanized screws are good for tough places. The right screw length and material keep your project safe.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Acero inoxidable | 304 and 305 grades are common; 316 for extreme environments |
| Galvanized Screws | Thick zinc coating gives excellent corrosion resistance |
Note: Always match your screw sizes and fasteners to the environment. This gives you the best results.
Sheet Metal Screw Size Guide for Applications
Choosing the right screw can feel confusing, but a clear screw size chart helps you make the best choice for your project. You need to match the screw to your material and application. This screw size guide will help you pick the right fastener for general use, ductwork, metal roofing, and heavy-duty jobs.
Screw Size Chart Overview
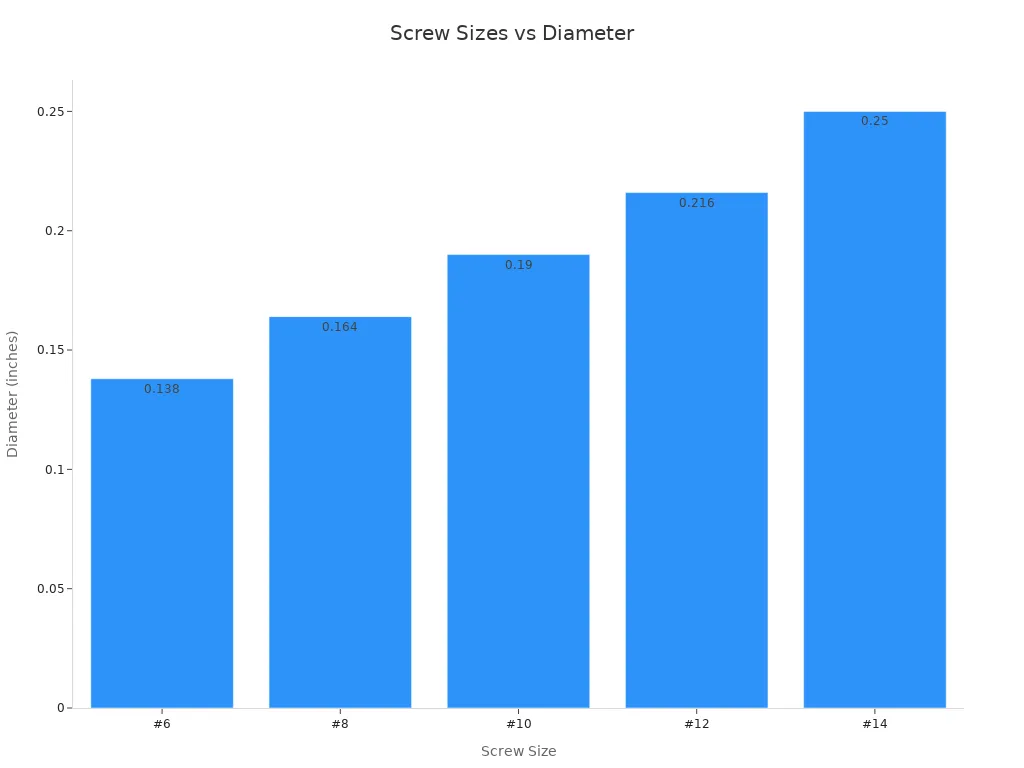
You can find sheet metal screws in many sizes. The most common screw sizes range from #4 to #14. Each number shows the diameter of the screw. Larger numbers mean thicker screws. The length changes based on what you need to fasten.
| Tamaño | Diámetro (pulgadas) | Length (inches) |
|---|---|---|
| #4 | 0.112 | Varía |
| #6 | 0.138 | Varía |
| #8 | 0.164 | Varía |
| #10 | 0.190 | Varía |
| #12 | 0.216 | Varía |
| #14 | 0.250 | Varía |
Note: Common screw sizes cover most home and industrial projects. You can find these screws in different lengths to fit your needs.
When you look at a screw size chart, you see that the diameter and length both matter. The diameter gives strength. The length lets you reach through the material without sticking out too far. Always check the screw size chart before you start your project.
General Purpose and Ductwork
For most general jobs and ductwork, you want screws that grip well and go in fast. In HVAC work, you often use hex head ZIP screws. These screws cut through thin metal and hold tight.
- Utilice 1/4″ hex head ZIP screws for most home ductwork.
- Use 5/16″ hex head self-drilling screws for bigger, commercial ducts.
You should drill a pilot hole if the metal is thick or hard. This helps the screw go in straight and stops the metal from cracking. For thin sheet metal, tornillos autoperforantes save time because you do not need a pilot hole. Always match the screw length to the thickness of your duct or panel.
Tip: For ductwork, use screws with sharp threads. These threads grip thin metal better and keep the duct secure.
Metal Roofing Screws
Metal roofing screws need to handle wind, rain, and heavy loads. You want screws that seal out water and hold panels tight. Roofing manufacturers recommend different sizes for different jobs.
| Tamaño del tornillo | Application Description |
|---|---|
| 1 1/2 inch | Fastening panels |
| 1 pulgada | Standing seam roofing |
| 2 inch | Overlapping or corrugated panels |
| 1 pulgada | Thicker roofing sheets |
| #9 & #10 | Metal to wood screws |
| #12 | Metal to metal screws |
| #14 | Heavy snow load areas |
You should use a screw size chart to pick the right length and diameter. For metal roofing screws, the gauge size shows the diameter. Bigger numbers mean thicker screws. If you work with harder or thicker steel, use a larger gauge. Always use screws with a sealing washer to stop leaks.
- Metal roofing screws come in many lengths. Pick a screw long enough to go through the panel and into the support.
- For standing seam roofs, use 1-inch screws.
- For overlapping panels, use 2-inch screws.
- Use #12 or #14 screws in places with heavy snow.
Note: Always check the screw size chart before starting a roofing job. This helps you avoid leaks and keeps the roof strong.
Automotive and Heavy Duty Uses
Automotive and heavy-duty jobs need strong screws that can handle stress and vibration. You often use larger screws for these tasks. The most common screw sizes for these jobs are #6, #8, #10, #12, and #14.
| Tamaño del tornillo | Diámetro (pulgadas) | Diameter (fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| #6 | 0.138 | 9/64 |
| #8 | 0.164 | 11/64 |
| #10 | 0.190 | 3/16 |
| #12 | 0.216 | 7/32 |
| #14 | 0.250 | 1/4 |
You should use a pilot hole for thicker metal. This makes it easier to drive the screw and keeps the threads from stripping. For heavy-duty work, pick screws with deep threads and strong points. These features help the screw bite into the metal and hold tight, even when the job gets rough.
Tip: Always use a screw size chart to match the screw to your material. This keeps your project safe and strong.
How to Use the Screw Size Guide
- Check the screw size chart for the right diameter and length.
- Choose the screw based on your material and job type.
- Use pilot holes for thick or hard metals.
- Pick the right thread type for your application.
- For outdoor or wet jobs, use coated or stainless steel screws.
A good screw size guide helps you avoid mistakes. You get a better hold, fewer stripped threads, and a safer project. Always keep a screw size chart handy for quick reference.
Additional Tips for Selecting Screw Sizes
Pilot Holes and Pre-Drilling
Making a pilot hole before you use a screw helps a lot. Pilot holes let the screw grip the metal better. This means your screw will hold tighter. Thin sheets may not give enough grip for the threads. If this happens, the screw can strip and get loose. Drilling a pilot hole helps the screw go in straight. It also stops the metal from getting damaged. Always use a pilot hole that matches your screw size for the best hold.
Tip: Drill pilot holes in thin or hard metals. This helps the screw hold better and stops stripped threads.
Thread Types and Points
Sheet metal screws come with different thread types. Each thread type works best for certain jobs. These screws have narrow threads that grip metal tightly. The threads go all the way down the shank. This gives a strong hold. Many screws have a sharp tip. This lets you drive them into metal without making a hole first. Self-drilling screws save time because you do not need a pilot hole for most jobs.
| Tipo tornillo | Ventajas | Desventajas |
|---|---|---|
| Tornillos autorroscantes | Easy to use, work well for softer materials. | Not good for hard materials, do not handle vibration well. |
| Tornillos autoperforantes | Quick and easy, no need to drill a hole first. | Do not work well in thick metal, debris can make it harder to use. |
Nota: Pick the right thread type and screw size for your material. This helps you get a good grip and avoid problems.
Coatings and Corrosion Resistance
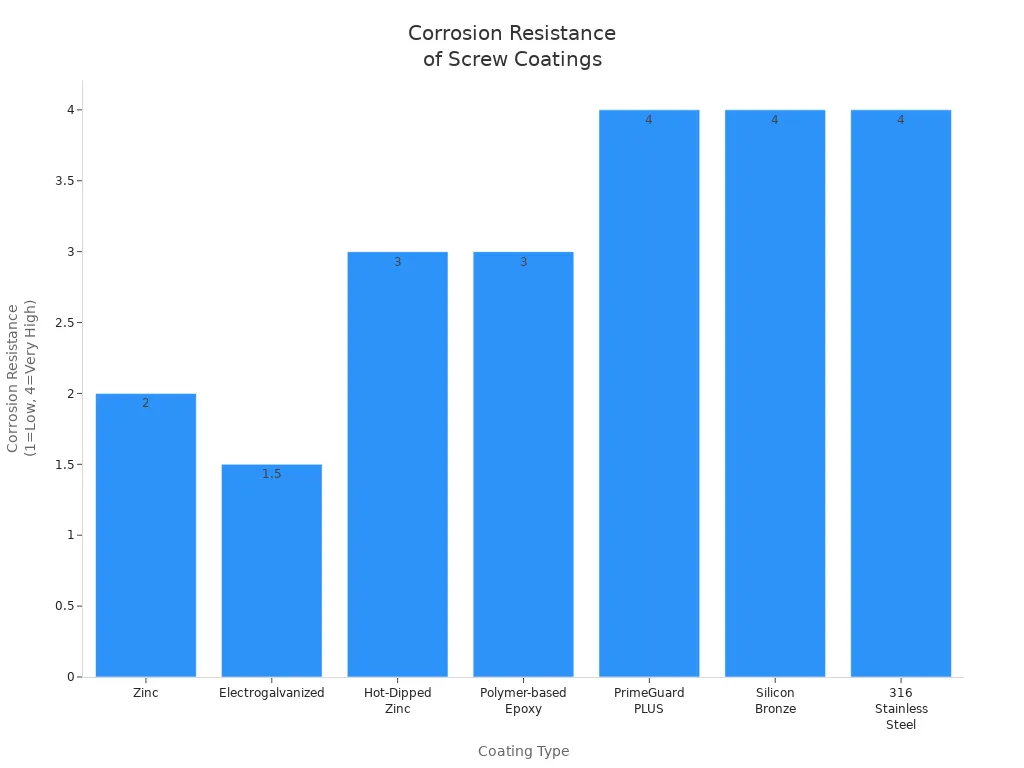
Pick screws with coatings to stop rust, especially outside or near water. Some coatings work better than others. Zinc and hot-dipped zinc give medium to high protection. Polymer-based epoxy and PrimeGuard PLUS give very high protection. Silicon bronze and 316 stainless steel are best for jobs near water.
| Coating Type | Descripción | Corrosion Resistance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc | Used a lot, makes a barrier to protect the screw. | Moderado |
| Hot-Dipped Zinc | Thicker layer, better at stopping rust but can be uneven. | Alta |
| Polymer-based Epoxy | Covers the screw evenly, goes over other coatings. | Alta |
| PrimeGuard PLUS | Lasts a long time in salt spray tests. | Very High |
| Bronce Silicio | Great for water jobs, stops rust very well. | Very High |
| Acero inoxidable 316 | Used for water jobs, gives excellent rust protection. | Very High |
Tip: Always match your screw size and coating to where you use it. This helps your project last longer.
Risks of Incorrect Screw Sizes
Stripped Threads and Loose Fits
When you use the wrong screw size, you risk stripped threads and loose fits. If a screw is too small, it cannot grip the metal well. The threads may not catch, so the screw spins in place. This weak grip can cause the screw to fall out over time. If you use a screw that is too large, you might force it into the hole. This can damage the threads in the metal. Once the threads strip, the screw will not hold at all.
Tip: Always match the screw diameter to the pilot hole for a secure fit.
Loose screws can make your project unstable. You may notice rattling or movement in the metal parts. This can lead to bigger problems, especially in projects that need to handle weight or vibration.
Material Damage and Safety Issues
Incorrect screw sizes can damage your materials and create safety risks. When a screw is too long or too thick, it can split or crack the metal. You might see the fastener tear through the side of a part if the material does not support it. This is called fastener tearout. If you use too much force, the threads in the metal can pull out. This is known as thread pullout.
- Fastener tearout: The screw rips through the side of the metal.
- Thread pullout: The threads get pulled out from the metal.
Both problems weaken your project. If a screw fails, parts can come loose or fall off. This can cause injuries or damage equipment. Always check your screw size before you start. A good fit keeps your project safe and strong.
You make your project safer and stronger with the right screw size. Always look at screw guides for your material and job. Use this table to help you remember what matters most:
| Factor clave | Explicación |
|---|---|
| Seguridad | The right fastener size stops problems and holds heavy things. |
| Meeting Design Intent | The correct size helps your project work the way you want. |
| Selección de materiales | Choose stainless steel, titanium, or steel for the best results. |
If your project is special, ask the manufacturer for help.
Preguntas más frecuentes
What size sheet metal screw should you use for thin metal?
Debe utilizar #6 or #8 screws for thin metal. These sizes grip well and do not damage the material.
Do you need to drill a pilot hole for sheet metal screws?
Deberías drill a pilot hole for thick or hard metal. This helps the screw go in straight and prevents stripping.
How do you choose the right screw for your application?
You need to match the screw size to your material and application. Always check a screw size chart before starting your project.