You can choose the right bolt for your project with confidence. The correct bolt size and type depend on your materials and the strength you need. A bolt size chart helps you make accurate choices. For example, matching bolt size to the recommended clearance hole size keeps your assembly safe and secure.
| Tamaño del tornillo | Recommended Clearance Hole Size |
|---|---|
| 1/4″ | 5/16″ |
| 3/8″ | 7/16″ |
| 1/2″ | 9/16″ |
- Identify the bolt size from the chart.
- Find the matching clearance hole size.
- Check that the fit type suits your project.
Using the right chart prevents mistakes and protects your work from damage.
Principales conclusiones
- Use a bolt size chart to pick the right bolt. This helps keep your project safe and makes sure it fits well.
- Pick the correct bolt type for your materials. Some bolts work best for wood, metal, or other things.
- Always look at the bolt grade to see if it is strong enough. Higher grades mean the bolt is stronger for tough jobs.
- Measure the bolt’s diameter and length before you buy it. Good measurements help you avoid mistakes and keep things safe.
- Do not make mistakes like using the wrong length or tightening too much. Careful choices help your bolts stay strong and last longer.
Tipos de pernos
When you start a project, you will notice there are many tipos de pernos. Each type has a special shape and purpose. Knowing the right bolt helps you build strong and safe structures.
Pernos hexagonales
pernos hexagonales have a six-sided head. You can tighten them with a wrench or socket. These bolts work well in tight spaces. You will find hex bolts in construction, automotive, and machinery projects. They connect wood, metal, and plastic. Many hex bolts resist corrosion, so you can use them outdoors or near water.
| Característica | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Cabeza hexagonal | Easy to grip with tools |
| Versatilidad | Connects many materials |
| Anti-corrosion | Good for outdoor and coastal areas |
| Alta resistencia | Used in cars, bridges, and towers |
Pernos de carro
Carriage bolts have a round, smooth head and a square neck. You use them mostly in wood projects. The square neck stops the bolt from turning when you tighten the nut. Carriage bolts give a clean look and help prevent injuries because the head is smooth.
| Use Case | Ventajas |
|---|---|
| Decks, fences, furniture | Secure, smooth, and safe connections |
| Metal frames | Prevents rotation, tamper-resistant |
| Visible applications | Finished appearance, hard to remove |
Pernos de máquina
You use machine bolts when you need precise alignment. These bolts fit into pre-tapped holes. You can take them apart and put them back together without damaging the threads. Machine bolts work well with thin materials and in electronics or automotive interiors.
- Precision alignment
- Fastening into pre-tapped holes
- Easy disassembly for maintenance
Tirafondos
Lag bolts, also called lag screws, are very strong. You use them for heavy-duty jobs like building decks or retaining walls. Their long length gives extra holding power in wood. A 1/4″ lag screw can hold up to 272 lbs.
- Gran capacidad de carga
- Strong and reliable for construction
- Good for large wood pieces
Pernos de ojo
Eye bolts have a loop at one end. You use them to lift or hang objects. Each eye bolt has a working load limit. You must follow safety rules and never exceed this limit. Always install eye bolts in strong structural members.
Tip: Always check the working load limit stamped on the eye bolt before lifting.
Pernos en U
U-bolts look like the letter “U.” You use them to attach pipes, cables, or rods to surfaces. U-bolts come in different sizes for plumbing and automotive work.
| Pipe Size | U-Bolt Diameter | Inside Width | Leg Length | Longitud de la rosca |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 1/4″ | 15/16″ | 3-1/4″ | 2-3/8″ |
| 2″ | 3/8″ | 2-7/16″ | 4-1/2″ | 2-1/2″ |
| 3″ | 1/2″ | 3-9/16″ | 5-13/16″ | 3″ |
- Body mounting
- Piping support
- Suspension mounting
Pernos en J
J-bolts have a hook shape. You use them to anchor structures to concrete. J-bolts secure columns, machinery, and equipment to floors or foundations.
- Anchoring structural columns
- Securing light poles
- Supporting steel buildings
Pernos de anclaje
Anchor bolts hold objects to concrete. You can install them before or after pouring concrete. Some anchor bolts expand to grip the concrete tightly. These bolts give strong support for heavy loads.
| Type of Bolt | Método de instalación | Strength Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cast-in-Place Anchor | Installed inside concrete | Strong anchorage |
| Post-Installed Anchor | Installed in drilled hole | Similar strength, may vary |
| Expansion Anchor | Expands in drilled hole | Tight grip in concrete |
Pernos de cenador
Arbor bolts are special bolts used in electric saws. You use them to secure saw blades. You may also use arbor bolts in woodworking or machinery to clamp sandpaper or sanding mops.
- Securing saw blades
- Modifying motors for sanding
- Woodworking applications
Pernos ciegos
Blind bolts work when you cannot reach both sides of the material. You install them from one side only. Blind bolts are strong and resist vibration. They are tamper-proof and good for large construction projects.
- Single-sided installation
- Alta resistencia
- Vibration resistance
Specialty Bolts
Some bolts have unique shapes for special jobs. You may see pernos de cabeza hexagonal, socket head cap screws, toggle bolts, flange bolts, and shoulder bolts. Each type fits a specific need, like precise alignment or heavy load tension.
- Hex Head Bolts: Wrench tightening
- Socket Head Cap Screws: Low-profile use
- Carriage Bolts: Wood projects
- Eye Bolts: Hanging objects
- U-Bolts: Attaching pipes
- Anchor Bolts: Securing to concrete
- Toggle Bolts: Anchoring to walls
- Flange Bolts: Load distribution
- Shoulder Bolts: Machinery alignment
- Tension Control Bolts: Structural tension
You can choose from many types of bolts. Each type helps you solve a different problem in construction, DIY, or repair work.
Bolt Size Chart
Choosing the right bolt starts with understanding the bolt size chart. You can use this chart to match the correct bolt to your project. The chart shows you the main measurements and helps you compare different bolt sizes. You will also see how US and metric systems use different grades and standards.
Key Measurements
When you look at a bolt size chart, you will notice three main measurements. These measurements help you pick the right bolt for your job. You need to know the components of bolts to read the chart correctly.
| Tipo de medición | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Diámetro | The width of the bolt, often shown as ‘M’ plus a number (like M6) or in inches (like 1/4″) |
| Longitud | The distance from the bottom of the head to the end of the bolt, measured in millimeters or inches |
| Paso de rosca | The space between threads, measured in millimeters for metric bolts or as threads per inch for imperial bolts |
Tip: Always measure the diameter and length before you buy bolts. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your project safe.
You will see these measurements listed for each bolt in the bolt size chart. Knowing the diameter, length, and thread pitch lets you choose bolts that fit perfectly.
Bolt Sizes
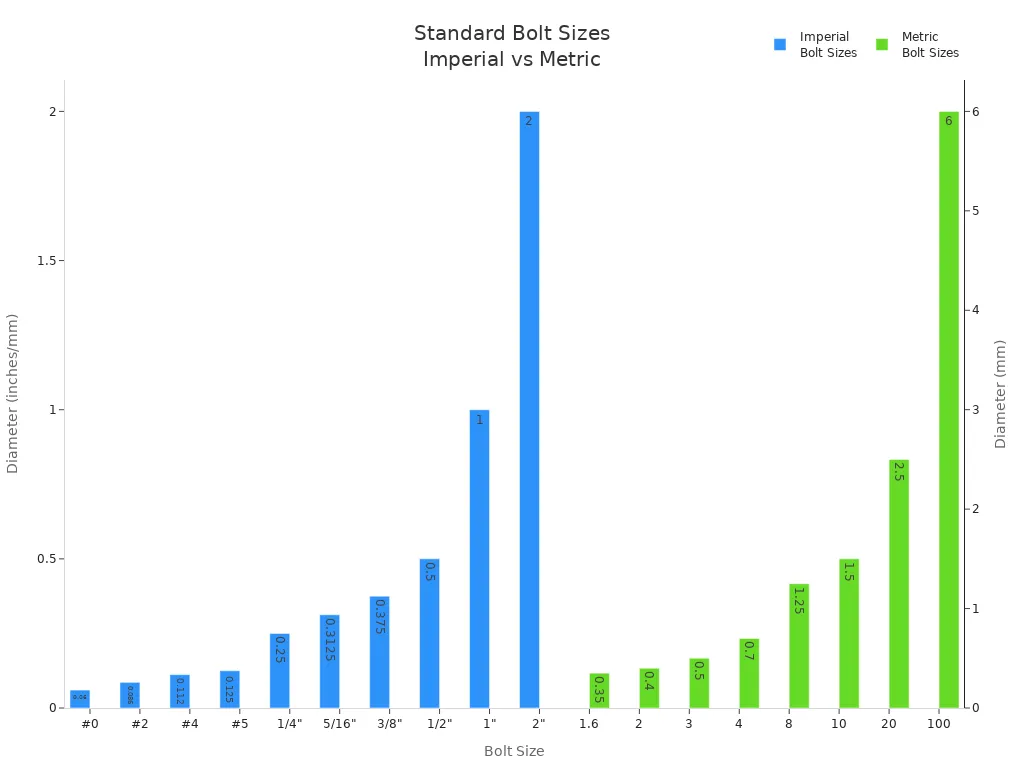
Bolt sizes come in both imperial and metric systems. You will find imperial sizes mostly in the USA and UK. Metric sizes are common in Europe and Asia. The bolt size chart below shows standard sizes for both systems. You can use this chart to compare and select the right bolt for your needs.
| Size (Imperial) | Diameter (in) | Coarse Thread (UNC) | Fine Thread (UNF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | 0.06 | — | — |
| #2 | 0.086 | 56 | 64 |
| #4 | 0.112 | 40 | 48 |
| #5 | 0.125 | 40 | 44 |
| 1/4″ | 0.25 | 20 | 28 |
| 5/16″ | 0.3125 | 18 | 24 |
| 3/8″ | 0.375 | 16 | 24 |
| 1/2″ | 0.5 | 13 | 20 |
| 1″ | 1 | 8 | 12 |
| 2″ | 2 | 4.5 | — |
| Size (Metric) | Diámetro (mm) | Paso grueso | Paso fino |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | 0.35 | — | — |
| 2 | 0.4 | — | — |
| 3 | 0.5 | — | — |
| 4 | 0.7 | — | — |
| 8 | 1.25 | 36.61 | 39.17 |
| 10 | 1.5 | 57.99 | 61.2 |
| 20 | 2.5 | 244.8 | 271.5 |
| 100 | 6 | 6995 | 7562 |
You can also see a visual comparison of standard bolt diameters in both systems:
You will notice that some industries use special bolt size charts. For example, aircraft and farm equipment often use imperial sizes. Automotive and construction projects may use metric sizes. The chart helps you match the right bolt sizes to your project.
Some common types of bolt size charts incluir:
- Coarse Thread Series: Good for quick assembly and less likely to cross thread.
- Fine Thread Series: Offers higher tension strength and works well for precise jobs.
- Unified Thread Standards: Used in the US, UK, and Canada for both coarse and fine threads.
- ISO Standards: Used worldwide, especially in automotive and aerospace work.
- British Standard: Found in vintage machinery and vehicles.
US vs. Metric Grades
You need to know the grade of a bolt to make sure it is strong enough for your project. The bolt grade guide shows you how to compare US and metric grades. Each grade tells you how much force the bolt can handle.
| Grado de perno | Strength Description | Aplicaciones típicas |
|---|---|---|
| Grado 2 | Low- to medium-strength carbon steel | Light construction, automotive assemblies, plumbing & HVAC installations |
| Grado 5 | Acero al carbono medio | Machinery, automotive applications, construction equipment |
| Grado 8 | Alta resistencia a la tracción | Heavy-duty machinery, construction & infrastructure projects |
| Metric 10.9 | High-strength | High-stress applications, similar to SAE Grade 8 |
You can spot US bolt grades by the lines on the bolt head:
- No lines mean Grade 2.
- Three lines mean Grade 5.
- Six lines mean Grade 8.
Metric bolts use a two-number system. The first number shows the tensile strength. The second number shows how much the bolt can stretch before breaking. For example, a 10.9 bolt is very strong and works like a Grade 8 bolt in the US system.
Note: Always check the bolt grade guide before you start your project. This helps you pick bolts that are safe and strong enough for your needs.
When you use a bolt size chart, you can compare grades, sizes, and thread types. You will find the right components of bolts for any job. This makes your work safer and more reliable.
Choosing Bolts
Application Match
Necesitas match the right bolt to your project for strong and safe bolted joints. Each application has unique needs. For example, wood, metal, and masonry all require different bolt types and features. The table below helps you see what to consider when choosing bolts for different materials:
| Factor | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Requisitos de carga | Think about the weight or force your bolted joints must handle. Heavy loads need stronger bolts. |
| Tipo perno | Pick bolts that suit your material. Carriage bolts work well in wood. Hex bolts fit metal best. |
| Nut Type | Use lock nuts for areas with vibration. Choose nuts that match your bolt and application. |
| Material and Environment | Use stainless steel for outdoor projects. This prevents rust and keeps bolted joints strong. |
| Tipo de hilo | Fine threads give more strength but are harder to install. Coarse threads work better in soft materials. |
| Right Finish | Select finishes for corrosion resistance. Zinc plating gives mild protection. Black oxide looks good. |
| Sizing and Compatibility | Make sure bolt length and diameter fit your project. This keeps joints secure. |
Tip: Always check the load and environment before you pick a bolt. This helps you avoid weak or rusty bolted joints.
Material and Grade
The material and grade of a bolt affect the strength and durability of your bolted joints. You should always match the bolt grade to the job. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you choose:
- Assess the load your bolted joints will face. Use higher grades for heavy loads.
- Think about where you will use the bolt. Wet or salty air needs stainless steel or coated bolts.
- Decide how important the connection is. For critical joints, use high-grade bolts.
- Choose bolts with a long lifespan for moving or vibrating parts.
- Make sure the bolt grade matches the materials you are joining.
- Follow industry standards for your project. For example, property class 8.8 means medium strength, 10.9 means excellent sturdiness, and 12.9 means the highest strength.
- Ask an engineer or fastener expert if you are unsure.
Note: Using the right material and grade keeps your bolted joints safe and long-lasting.
Errores comunes
Many beginners make mistakes when choosing bolts. These errors can weaken bolted joints or cause failure. Watch out for these common problems:
- Incorrect bolt length: If you do not have at least two full threads engaged, the joint may fail.
- Over-tightening: Too much force can strip threads or break bolts.
- Wrong washer type: The wrong washer can make bolted joints loose, especially with vibration.
- Mixing fastener types: Do not mix metric and imperial bolts. This causes poor fit and weakens the joint.
- Neglecting lubrication: Without the right lubricant, bolts may not reach the correct tightness and can seize.
Always double-check your bolt size, type, and installation steps. Careful choices prevent problems and keep your bolted joints strong.
Quick Reference
Step-by-Step Checklist
You can follow a simple checklist to choose the right bolt for your project. This process helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your work safe.
Check the Size
Use the size recommended by the manufacturer. If you do not have a recommendation, pick a bolt that fits the hole snugly.Measure Material Thickness
Select a bolt length that matches the thickness of the materials you want to join. A good rule is to use a bolt that is 1.5 to 2.5 times the thickness of the thinner material.Decide the Function
Think about how the bolt will work. Will it go through both pieces and use a nut, or will it screw into a threaded hole? Make sure the bolt can handle the load.Count the Bolts Needed
Figure out how many bolts you need for a strong connection.
Tip: You can use a caliper to measure thread pitch for metric bolts. A bolt size gauge helps you find the right size by fitting bolts through holes. If you do not have these tools, a ruler works in a pinch.
Bolt Sizing FAQ
You may have questions about bolts. Here are answers to some of the most common ones:
What is bolt tensile strength?
Bolt tensile strength is the maximum force a bolt can handle before it breaks when pulled apart. The grade, size, and material of the bolt affect this strength.What are the four parts of a bolt?
Every bolt has a head, a shank (the smooth part), threads, and a point (the tip).What are the grades of bolts?
Common grades include SAE Grade 2, 5, and 8, and Metric Class 8.8, 9.8, 10.9, and 12.9. Higher grades mean stronger bolts.How are bolts classified?
Bolts are classified by grade, type (like hex or carriage), size (diameter and length), thread pitch, and material.What is the strongest grade for bolts?
SAE Grade 8 and Metric Class 12.9 are the strongest grades you will find for most projects.
Remember: Picking the right bolt keeps your project safe and strong.
Elegir el tornillo adecuado is simple if you remember some tips. First, pick the right type for your job, like hex or carriage bolts. Next, match the material y grado so your bolt is strong and lasts long. Use bolts that resist rust if you work outside. Always check the diameter and thread pitch so the bolt fits well. Look at a nut size chart so you do not pick the wrong size.
You can use different resources to help you pick bolts:
| Resource | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Fastener Thread Terminology | Learn about thread types and classes. |
| Drive & Head Styles | See the different bolt heads and drives. |
| Material Specifications | Compare bolt materials for your project. |
The more you practice, the easier bolt picking gets. You can always come back to this guide if you need help. 😊
Preguntas más frecuentes
How do you identify the right bolt for your project?
You can use a bolt identification guide. This guide helps you check the size, length, and thread type. Always match the bolt to your material and load needs. This keeps your project safe and strong.
What are the main differences between nut grades?
Nut grades explained show you the strength and material of each nut. Higher grades mean stronger nuts. You should always match the nut grade to the bolt grade for a secure fit.
Why do you need to know about different types of nuts and bolts?
You need to know about different types of nuts and bolts to pick the right ones for your job. Each type works best for certain materials and loads. Using the correct type keeps your project safe.
How do you choose the right nut grade for your bolt?
Nut grades explained help you match the nut to your bolt. Always check the grade mark on the nut. Pick a nut with the same or higher grade than your bolt for the best strength.
Can you mix different types of nuts and bolts in one project?
You should not mix different types of nuts and bolts. Mixing types can cause weak joints or damage. Always use matching types and grades for the safest results.