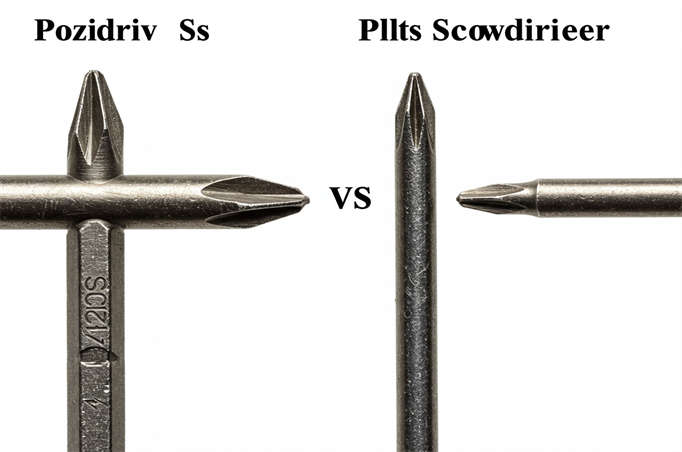
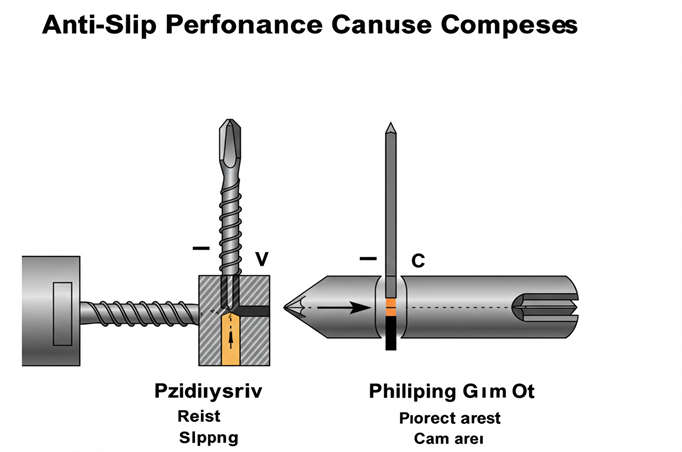
We understand the importance of selecting the right fastener for your project at Prince Fastener. Whether you’re working on high-torque applications, delicate electronics, or everyday DIY tasks, the right screw can make all the difference. In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between Phillips screws and Pozidriv screws, two common types of crosshead screws.
Pozidriv screws, often mistakenly referred to as “Pozidrive,” are an improved variation of the Phillips screw designed to address the cam-out issues that Phillips screws are prone to. With their unique design featuring additional 45-degree indentations, Pozidriv screws offer better grip, reduced slippage, and enhanced torque transmission.
This makes them ideal for applications where precision and durability are paramount. As experts in the fastener industry, we’re committed to helping you understand the strengths and limitations of each screw type, so you can make informed decisions that ensure the success and longevity of your projects. Whether you’re a professional tradesperson or a DIY enthusiast, this knowledge will empower you to choose the optimal fastener for every task.
Pozidriv Screw vs. Phillips Screw: What’s the Difference?
Pozidriv screws and Phillips screws differ in their structure, application, and performance in the following ways:
1. Structural Differences
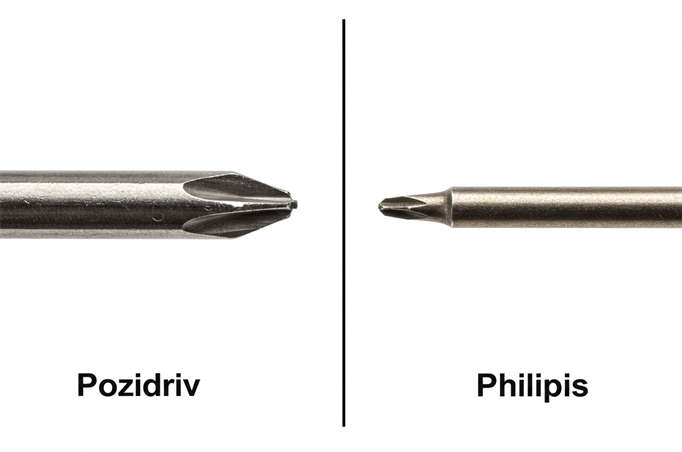
- Pozidriv Screw: The head of the Pozidriv screw features four intersecting slots that form a pattern resembling the character “Mi” (rice), with each slot evenly distributing force. This four-slot design helps prevent misalignment under pressure.
- Phillips Screw: The Phillips screw head features a simple cross design created by two perpendicular slots. This straightforward design works well in many applications but can lead to errors under high torque.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages
Pozidriv Screw Advantages:
- Superior Anti-Slip Performance: The four slots in the Pozidriv screw create a larger contact area between the screw and screwdriver, enhancing torque transmission and minimizing the chance of slipping. This makes it ideal for high-precision, high-torque operations such as machinery assembly and electronic device installation.
- Durability: The four-slot design allows the screw to withstand higher torque levels without significant damage to the slots, increasing the screw’s lifespan.
Disadvantages of Pozidriv Screws:
- Tool Compatibility Issues: Pozidriv screws require a specific Pozidriv screwdriver to operate effectively. Regular Phillips screwdrivers may not fit properly, resulting in inaccurate engagement.
Phillips Screw Advantages:
- Good Compatibility: The Phillips screwdriver is a widely used tool, and most screwdriver sets include a Phillips bit, making it highly convenient for everyday tasks.
- Low Manufacturing Cost: The simple design of Phillips screws makes them cheaper to produce, which is why they are commonly found in consumer products.
Disadvantages of Phillips Screws:
- Prone to Slipping: In high-torque operations, the Phillips screw tends to slip because of its limited contact area, which can damage the screw head and prevent proper tightening.
- Lower Torque Transmission Efficiency: Due to its two-slot design, Phillips screws are less efficient at transmitting torque compared to Pozidriv screws.
3. Application Differences
- Pozidriv Screws: These screws are commonly used in applications where high torque is required, such as automotive engine components and aerospace equipment, where secure, long-lasting fastening is essential.
- Phillips Screws: These are typically used in everyday applications like furniture assembly and securing small electrical casings, where the torque requirements are relatively low.
4. Overall Design Comparison
- Pozidriv Screws: Designed for efficient torque transfer and stress distribution, the four-slot design reduces localized stress and enhances resistance to slipping and wear.
- Phillips Screws: The simpler cross-slot design works well for basic tightening and loosening, but it is prone to slippage under higher torque, resulting in less precise performance.
How Do Pozidriv Screws and Phillips Screws Compare in Terms of Anti-Slip Performance?
The difference in anti-slip performance between Pozidriv and Phillips screws is most noticeable in the following aspects:
- Slot Design and Contact Area:
- Pozidriv Screws: The four-slot design increases the contact area between the screwdriver and the screw, allowing for better torque transfer and reduced chance of misalignment.
- Phillips Screws: With only two slots, the contact area is smaller, making it more prone to slipping, especially under high torque.
- Torque Transmission Efficiency:
- Pozidriv Screws: The four slots distribute torque more evenly, reducing stress concentration and improving efficiency. This provides better anti-slip performance.
- Phillips Screws: The two-slot design makes torque transmission less efficient, especially in high-torque operations, leading to higher chances of slippage.
- Slot Wall Design and Friction:
- Pozidriv Screws: The steeper walls of Pozidriv slots provide more friction, reducing the likelihood of slippage.
- Phillips Screws: The gentler walls of Phillips slots result in less friction, making the screw more prone to slipping during high-torque applications.
- Application Context and Anti-Slip Requirements:
- Pozidriv Screws: These are ideal for high-torque applications, such as machinery assembly and automotive parts, where slip-resistance is critical.
- Phillips Screws: These are commonly used in everyday situations with lower torque requirements, where anti-slip performance is less crucial.
- Tool Compatibility and Impact on Anti-Slip:
- Pozidriv Screws: You need a specific Pozidriv screwdriver to ensure proper engagement. Using the wrong tool can lead to slippage and errors.
- Phillips Screws: Phillips screwdrivers are widely available, but using worn or incompatible tools may still cause slippage, particularly under high torque.
Pozidriv screws offer better anti-slip performance compared to Phillips screws, thanks to their four-slot design, larger contact area, and more efficient torque transmission. However, Phillips screws are still widely used due to their broad compatibility and lower manufacturing cost. For high anti-slip requirements, choose Pozidriv screws; for general-purpose use, Phillips screws are sufficient.
How Do Pozidriv Screws and Phillips Screws Compare in Durability?
The durability of Pozidriv and Phillips screws differs significantly:
- Slot Design and Stress Distribution:
- Pozidriv Screws: The four-slot design ensures an even distribution of force across the slots, reducing localized stress and preventing damage to the slot walls. This enhances the durability of the screw.
- Phillips Screws: The two-slot design tends to concentrate stress at specific points, leading to faster wear and potential damage to the slot walls under high torque.
- Torque Transmission Efficiency and Slippage:
- Pozidriv Screws: The efficient torque transfer of the four-slot design prevents slippage, extending the lifespan of the screw by reducing wear on the slots.
- Phillips Screws: The reduced torque transfer efficiency and higher likelihood of slippage under high torque accelerate wear on the screw’s slot walls, decreasing durability.
- Slot Wall Damage and Lifespan:
- Pozidriv Screws: The steeper walls of Pozidriv slots provide more friction, which minimizes slippage and damage over time, resulting in a longer lifespan.
- Phillips Screws: The gentler walls of Phillips slots lead to more frequent slippage, especially under high torque, causing the slot walls to wear down more quickly.
- Application Context and Durability Requirements:
- Pozidriv Screws: Used in high-durability environments such as machinery assembly, automotive components, and aerospace, Pozidriv screws meet stringent durability requirements.
- Phillips Screws: Primarily used in everyday applications where durability requirements are lower, Phillips screws provide sufficient performance but wear out more quickly under heavy use.
Pozidriv screws are more durable than Phillips screws thanks to their four-slot design, better torque transmission, and reduced wear. However, Phillips screws remain widely used in everyday applications due to their compatibility and lower manufacturing costs. If durability is a priority, opt for Pozidriv screws; for routine tasks, Phillips screws will suffice.
How to Quickly Identify a Phillips Screw vs. a Pozidriv Screw
Here’s how you can quickly identify a Phillips screw from a Pozidriv screw:
- Slot Shape:
- Phillips Screw: The head has a cross shape formed by two perpendicular slots.
- Pozidriv Screw: The head features a “mi” shape formed by four intersecting slots.
- Slot Depth and Edges:
- Phillips Screw: The slots are relatively shallow with smooth edges.
- Pozidriv Screw: The slots are deeper, with steeper walls and more defined edges.
- Tool Compatibility:
- Phillips Screw: Can be easily tightened with a Phillips screwdriver.
- Pozidriv Screw: Requires a specific Pozidriv screwdriver, and a Phillips screwdriver may not fit properly.
- Primary Use:
- Phillips Screw: Commonly used in general-purpose applications like furniture assembly and small electronic casings.
- Pozidriv Screw: Typically used in high-torque, high-durability applications like machinery assembly and automotive parts.
- Test with a Tool:
- If you have a Phillips screwdriver, try tightening the screw:
- If it fits and tightens easily, it’s a Phillips screw.
- If it doesn’t fit properly or slips, it’s likely a Pozidriv screw.
- If you have a Phillips screwdriver, try tightening the screw:
This method will help you quickly distinguish between Phillips and Pozidriv screws.
As we conclude this exploration of Phillips and Pozidriv screws, it’s evident that each has its place in the world of fasteners. Phillips screws, with their familiar cross-shaped indentation, remain a staple in many applications due to their widespread availability and compatibility. However, their susceptibility to cam-out at higher torques can be a significant limitation in demanding scenarios.
Pozidriv screws, on the other hand, with their additional 45-degree indentations, provide a more secure grip and greater torque capacity, making them the preferred choice for high-stress applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Their design not only reduces the risk of damage to both the screw and the driver but also enhances efficiency and reduces worker fatigue.
At Prince Fastener, we take pride in offering a comprehensive range of Pozidriv screws, carefully selected to meet the diverse needs of our customers. From woodworking and construction to intricate electronic assemblies, our Pozidriv screws deliver the reliability and performance required for success. Trust Prince Fastener to equip you with the highest quality fasteners and the knowledge to tackle any project confidently.