In the world of machinery, nuts may be small, but they play a crucial role. They act like tiny joints, connecting various mechanical components tightly and ensuring the smooth operation of equipment. However, nut loosening is a headache-inducing issue, like a hidden “time bomb” that can cause equipment failures or even safety accidents at any moment. From car engines to large industrial machinery, from precision instruments to building structure connections, the hidden dangers of nut loosening are everywhere. This not only affects production efficiency and quality but also poses a threat to people’s lives and property. Fortunately, with continuous technological advancements and engineering practices, people have developed various ingenious methods to prevent nut loosening. These methods act like strong defensive lines, safeguarding the stability and reliability of mechanical systems. Today, let’s explore the secrets to preventing nut loosening, understand the principles behind these methods, their application scenarios, and selection tips, and find the best solutions for the nut loosening issues in mechanical assemblies.
Methods to Prevent Nut Loosening
Nut loosening is a common problem in mechanical assemblies. Here are several common methods to prevent nut loosening:
Mechanical Prevention
Using a Cotter Pin
- Principle: Insert a cotter pin through the pin holes of the nut and bolt, then split the ends of the pin to fasten it inside the holes of the nut and bolt. This prevents the nut from rotating freely when external forces like vibration are applied.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for applications where reliable loosening prevention is needed and space is not a major concern, such as in mechanical drive device connections.
Using Lock Washers
- Principle: Lock washers come in various types, such as single-ear, double-ear, and internal-tooth washers. For example, double-ear lock washers have two ears that, when installed, are pressed against the side of the nut after tightening, preventing rotation.
- Application Scenarios: Widely used in various mechanical assemblies, especially in equipment where high loosening prevention is required, such as nut connections in automobile engines.
Using Spring Washers
- Principle: Spring washers are wave-shaped and elastic. When the nut is tightened, the spring washer flattens and exerts an elastic counterforce, increasing the friction between the nut and bolt, preventing loosening. It can also compensate for gaps between the bolt and nut, adding to the loosening prevention.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for general mechanical assemblies, such as machine tools and motors, especially effective in environments with small vibrations.
Using Jam Nuts
- Principle: Two nuts are screwed onto a bolt; one is tightened, then the other is screwed in the reverse direction. The two nuts exert pressure against each other, creating greater friction and preventing loosening.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for applications where substantial loosening resistance is needed, such as fastening nuts in large equipment, though this method requires a larger tightening torque.
Friction-Based Prevention
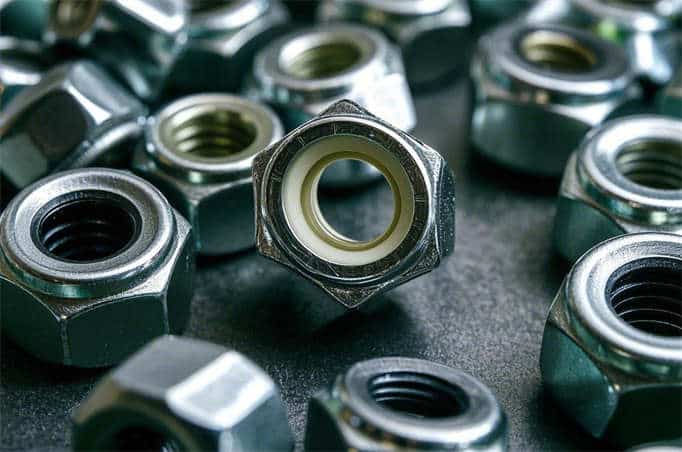
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
- Principle: These nuts have a nylon insert inside. When the nut is tightened, the nylon insert tightly contacts the bolt threads, generating high friction and preventing loosening. The nylon insert also serves as a seal, preventing dust and moisture from entering the threaded connection.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for applications requiring both loosening prevention and sealing, such as nut connections in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Self-Locking Nuts
- Principle: Self-locking nuts are specially designed with threads that have some elasticity. When tightened, the threads mesh tightly with the bolt threads, generating high friction and preventing loosening. Self-locking nuts offer good loosening prevention without the need for additional devices.
- Application Scenarios: Widely used in various mechanical assemblies, such as in automotive and aerospace fields, especially effective in environments with high vibration.
Chemical Loosening Prevention
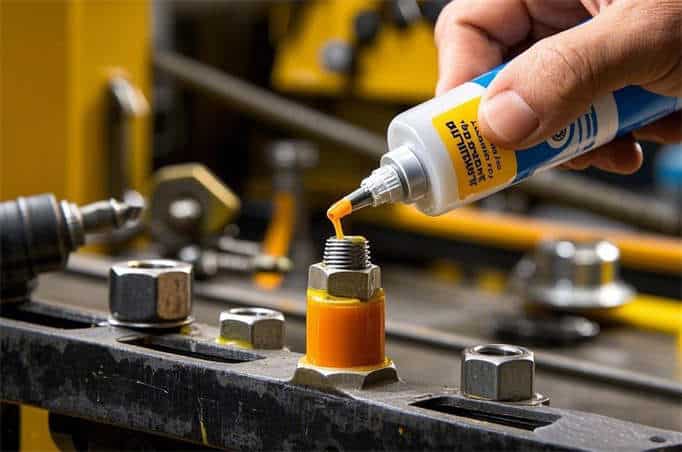
Using Anti-Loosening Adhesive
- Principle: Anti-loosening adhesive is a special chemical adhesive that, when applied to the threads of the nut and bolt, hardens to form a thin film. This film increases friction between the nut and bolt and also prevents rust and corrosion, thus preventing loosening.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for environments where both loosening prevention and corrosion resistance are required, such as in chemical equipment or marine applications. Care should be taken with the curing time and conditions of the adhesive.
Other Methods
Using Two Nuts
- Principle: Two nuts are screwed onto the bolt, the first one is tightened, and the second one is screwed in the opposite direction. The two nuts press against each other, increasing friction and preventing loosening.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for applications that require significant loosening resistance, such as fastening nuts in large equipment, but this method requires a larger tightening torque.
Welding Fixation
- Principle: Spot weld the nut and bolt connection to permanently fix them together and prevent loosening. This method offers reliable loosening prevention, but the welding process can affect the material properties of the nut and bolt and makes it difficult to dismantle.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for applications that do not require frequent disassembly and where loosening prevention is critical, such as nut connections in building structures.
In practical applications, the appropriate method for preventing loosening can be chosen based on the working environment, load conditions, and loosening prevention requirements.
Working Principle of Nut Lock Washers
Nut lock washers prevent nut loosening by utilizing unique structural designs and mechanical principles to resist loosening due to vibration, impact, and other dynamic loads. The core mechanism can be divided into three categories: mechanical locking, elastic compensation, and friction enhancement. Different designs emphasize different methods of loosening prevention.
Mechanical Locking Type: Dual-Layer Self-Locking Washers (e.g., Nord-Lock)
- Structure Features: Composed of two identical washers, the inner side has an angled tooth surface (angle α > bolt thread angle β), and the outer side has radial convex ribs.
- Working Principle:
- Installation Engagement: The angled tooth surfaces of the two washers mesh together, and the convex ribs engage with the nut and connected component surfaces.
- Vibration Loosening Prevention: When vibration causes a tendency for the nut to loosen, the wedge effect created by the angled teeth (α > β) forces the washer to lift, counteracting any displacement.
- Self-Locking Enhancement: A greater torque is required for disassembly, confirming its locking effect.
- Application Scenarios: High-vibration environments, such as high-speed rail, bridges, and heavy machinery.
- No need for pre-tightening force; surfaces need to be flat (e.g., hard metals).
Elastic Compensation Type: Disc/Spring Washers (e.g., DIN6796)
- Structure Features: Cone or disc shape, often made from spring steel, deforms elastically when compressed.
- Working Principle:
- Pre-Tightening Energy Storage: Deforms under installation to store elastic potential energy.
- Rebound Compensation: When pre-tightening force decreases due to vibration, the elastic potential energy is released, pushing the nut back into position and maintaining friction.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for medium-strength bolts (e.g., 8.8/10.9 grade), replacing regular spring washers.
- Requires pre-tightening force, suitable for axial loads.
Friction Enhancement Type: Serrated/Knurled Washers (e.g., SK, VSK Series)
- Structure Features: Surface designs with radial serrations, anti-slip knurls, or spines, typically made of stainless steel or carbon steel.
- Working Principle:
- Increased Friction: Serrations embed into the contact surface, increasing static friction.
- Elastic Assistance: Some designs combine with disc springs to assist in compensating for lost pre-tightening force.
- Typical Models:
- SK Series: Available in SKB/SKM/SKS/SKZ, for various bolt types.
- VSK Series: Specifically designed for railway systems, meets SN60727 standards, enhanced friction with knurled surfaces.
- Application Scenarios: General industrial equipment, automotive assembly, and other low-vibration environments.
Other Types and Considerations
- Spring Washers: Have edges that embed into the contact surface to prevent loosening, but are less effective at high pre-tightening forces (>200 N·m), and may result in pre-tightening force loss.
- DIN25201 Dual-Layer Washers: Combine lift tension and geometric wedge angles, ideal for heavy load and high-vibration scenarios.
- Material Selection: Choose between carbon steel (lower corrosion resistance) or stainless steel (higher corrosion resistance), depending on environmental conditions.
Nut lock washers achieve loosening prevention through mechanical locking, elastic energy storage, and friction enhancement mechanisms. When selecting the appropriate washer, consider vibration intensity, pre-tightening requirements, and surface hardness.
Application Scenarios of Nut Anti-Loosening Technology
Nut anti-loosening technology, through special structural design or process optimization, effectively prevents thread loosening caused by vibration, impact, or load variation. It is widely used in fields with high safety and reliability requirements. The main application scenarios are as follows:
1. Mechanical Manufacturing
- Automobile and Motorcycle Manufacturing
Anti-loosening nuts are widely used in key parts like engines, transmission systems, and suspension systems, addressing high-frequency vibrations during operation. - Agricultural Machinery and Power Tools
Equipment like tractors and harvesters, which operate in complex terrains, must withstand severe vibrations. Anti-loosening nuts ensure the stability of key connections.
2. Transportation Industry
- Rail Transportation (High-Speed Rail, Railways)
High-speed rail track connections, bogies, etc., must withstand high-frequency vibrations during high-speed operation. Technologies like Japan’s Hard-lock anti-loosening bolts are used in 45% of global high-speed rail projects. - Bridges and Road Infrastructure
Bridge bolts must endure vehicle loads and environmental stresses over time. Anti-loosening technology can reduce maintenance frequency. - Aviation and Aerospace
Parts like aircraft engines and satellite brackets must remain stable in extreme temperatures and high-pressure environments. Anti-loosening nuts require high material and process standards.
3. Engineering Machinery
- Heavy Equipment (Bulldozers, Loaders)
Parts of equipment such as scrapers and rotary drilling machines are prone to impact loads. Using reamed-hole bolts or steel spacers can significantly enhance anti-loosening ability. - Port Machinery and Mining Equipment
Equipment like unloading machines and crushers, which experience frequent collisions and speed variations, require structural optimization (such as increasing bolt elasticity) to ensure connection reliability.
4. Precision Manufacturing and High-End Equipment
- CNC Machines and Processing Equipment
The transmission systems of high-precision machines need to avoid micron-level displacement. Self-locking anti-loosening nuts use a triple friction mechanism for stable locking. - Energy Equipment (Wind Power, Nuclear Power)
Wind turbine tower bolts and nuclear reactor supports must withstand long-term dynamic loads. Anti-loosening technology extends equipment lifespan.
5. Other Special Scenarios
- Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering
Ship cabin equipment is prone to loosening under wave impact. Anti-loosening nuts can reduce maintenance costs. - Construction and Civil Engineering
Steel structure buildings and large venues require anti-loosening technology to improve seismic performance.
Technology Development Trends
- Material and Process Innovation: Plasma Nano Polishing (PLNP) technology improves surface precision and reduces friction loss.
- Intelligent Control: Combining sensors to monitor bolt pre-tension force in real-time for dynamic adjustment.
From the above scenarios, we can see that anti-loosening technology is evolving from passive prevention to active monitoring and self-adaptive adjustment to meet the demands of more complex operating conditions.
Comparison of Anti-Loosening Effects of Different Nut Materials
1. Material Properties and Anti-Loosening Mechanisms
The anti-loosening effect of nuts depends mainly on three mechanisms: friction-based anti-loosening, mechanical locking, and structural anti-loosening. The physical properties of different materials (such as hardness, elastic modulus, and friction coefficient) directly affect the effectiveness of these mechanisms:
Stainless Steel Nuts
- Advantages: High corrosion resistance, high hardness, suitable for high vibration, humid, or corrosive environments (such as in automobiles or medical equipment).
- Anti-Loosening Mechanism: Provides stable friction through high hardness and surface roughness, with a 30° wedge-shaped thread design that significantly increases normal pressure (normal pressure is 70% higher than standard threads).
- Limitations: Poor elastic deformation ability, requiring structural design (such as HARDLOCK nut’s double eccentric structure) to enhance anti-loosening performance.
Carbon Steel Nuts (Surface Treatment Type)
- Common Treatments: Galvanized, black oxide, Dacro coating.
- Advantages: Low cost, high strength, and increased friction coefficient with coating (e.g., galvanized coating increases friction by about 15%).
- Limitations: Coating wear after long-term use may reduce anti-loosening performance, requiring the addition of spring washers or double nuts.
Copper Nuts (Including Copper Alloys)
- Advantages: Good conductivity, corrosion resistance, suitable for electrical equipment. Soft material enables plastic deformation to enhance initial locking force.
- Limitations: May fail in high-vibration environments due to plastic deformation, requiring mechanical locking (e.g., cotter pins).
Aluminum Nuts
- Advantages: Lightweight, suitable for aerospace, sports equipment, and other applications requiring weight reduction.
- Limitations: Low strength, anti-loosening depends on structural design (such as nylon inserts or thread locking adhesives).
Nylon Insert Nuts
- Advantages: Non-metallic elastic material provides high friction damping, reusable more than 50 times.
- Limitations: Poor temperature resistance (generally ≤120°C), may soften in high-temperature environments leading to reduced locking force.
2. Key Factors and Selection Recommendations
Environmental Adaptability
- High-temperature Environments: Choose stainless steel or high-temperature alloys (e.g., Inconel), avoid nylon materials.
- Corrosive Environments: Stainless steel or Dacro-coated carbon steel is preferable.
Load and Vibration Strength
- High-Vibration Scenarios (e.g., Aircraft Engines): Stainless steel + mechanical locking (HARDLOCK nuts) or Dunlop threads.
- Low Load Static Connections: Nylon insert or copper nuts can meet the requirements.
Economic and Maintenance Costs
- Low-Cost Scenarios: Galvanized carbon steel + double nuts for anti-loosening.
- High-Maintenance Scenarios: Reusable nylon insert or self-locking nuts.
3. Conclusion
- Stainless Steel: Best overall performance but high cost.
- Carbon Steel: Cost-effective, but requires additional anti-loosening measures.
- Nylon Insert: Performs well in normal temperature and light load scenarios.
- Copper/Aluminum: Choose based on specific needs (electrical conductivity, weight reduction).
Selecting the right material depends on evaluating load, vibration frequency, environmental temperature and humidity, and maintenance cycles. Junker tests may be used for verifying anti-loosening performance.
Choosing Anti-Loosening Tools for Nuts
1. Clarify Usage Scenario Requirements
- Vibration Environment
- High-frequency vibration (e.g., automobile, aerospace): Prefer Shibli nuts (30° wedge-shaped) or double nut structures, or Hard-lock anti-loosening bolts, which achieve high reliability through structural deformation or friction self-locking.
- Medium vibration: Nylon insert locking nuts or metal self-locking nuts are suitable, combining anti-loosening with reusability.
- Load and Stability Requirements
- Heavy-duty machinery (e.g., construction, heavy equipment): Flanged nuts are recommended, as their increased contact area provides stronger vibration resistance and support.
- Light load or precision instruments: Spring washers or thread locking adhesives are cost-effective and easy to install.
- Space Constraints
- Narrow spaces: Non-metallic insert locking nuts or thin anti-loosening nuts are preferred to avoid extra space consumption by flanged designs.
2. Choose Anti-Loosening Principles and Technology
Friction-based Anti-Loosening
- Spring washers: Low cost, suitable for low-vibration environments but limited anti-loosening capacity.
- Thread locking adhesive: Choose the strength based on disassembly needs (purple/blue for low strength, red/green for high strength), and control adhesive quantity.
Mechanical Anti-Loosening
- Cotter pins + slotted nuts: High reliability but require destruction for disassembly, suitable for permanent connections.
- Wire rope: Used for bolt group anti-loosening, installation holes need to be reserved.
Structural Anti-Loosening
- Shibli nuts: 30° wedge-shaped thread design, significant anti-loosening effect, and reusable.
- Double nut locking: Provides anti-loosening through additional friction, low cost but occupies more space.
Elastic Deformation Anti-Loosening
- Nylon anti-loosening nuts: Embedded nylon rings increase friction, suitable for light to medium load scenarios. Choose nylon 66 material and ensure tolerance accuracy.
3. Consider Material and Processing Techniques
Material Matching
- Metal nuts: Combine anaerobic locking agents (e.g., Loctite 1243/1262).
- Plastic nuts: Use instant adhesives (e.g., Cyberbond 1470), but avoid excessive application that may make disassembly difficult.
Processing Precision
- Choose products with strict edge and thickness tolerances to avoid dimension deviations affecting anti-loosening performance.
Special Structural Nuts (e.g., Wedge-shaped self-locking)
Ensure processing techniques meet standards to avoid failure due to uneven deformation.
4. Weigh Cost and Maintenance Needs
- Low-Cost Solutions
- Spring washers, double nuts, or ordinary self-locking nuts are suitable for budget-conscious scenarios with lower anti-loosening requirements.
- High-Reliability Solutions
- Shibli nuts, Hard-lock bolts: Higher initial costs but reduce maintenance frequency, offering better long-term cost-effectiveness.
- Maintenance Convenience
- Frequent disassembly: Choose nylon nuts or low-strength thread adhesives.
- Permanent connections: Use rivet locking or welding, but sacrifice disassembly ability.
5. Brand and Certification Reference
International Brands
- High-requirement scenarios: Japan Hard-lock, Germany Bosch electric tool matching nuts.
- General scenarios: Domestic brands like Lianggong, Fuluo offer high cost-performance and adaptability.
Certifications and Testing
Prioritize products with ISO certification or anti-loosening test reports, such as vibration tests and repeated disassembly tests.
6. Practical Tips
Installation Tips
Double nut structures should be tightened in sequence (first flat nut, then slanted nut).
Thread locking adhesives need to be applied on clean threads, ensuring no oil contamination.Maintenance Check Cycle
- High-vibration environments: Check anti-loosening status every 3-6 months and replace failed parts.
- Static scenarios: Annual routine checks.
Conclusion: Choosing anti-loosening tools should consider factors like environmental vibration intensity, load requirements, budget, and maintenance frequency. It is recommended to prioritize structural anti-loosening (e.g., Shibli) or friction + locking agent combination solutions, and verify material and process standards during procurement to ensure long-term reliability.
Anti-loosening nuts are an important topic involving multiple factors. By understanding the principles and application scenarios of various anti-loosening methods, we can select the most suitable solution based on actual needs. When purchasing anti-loosening tools, considering the usage scenarios, anti-loosening principles, material and processing, cost, and maintenance factors will help us make an informed decision. As technology continues to develop, nut anti-loosening technology is constantly innovating and advancing, from traditional mechanical anti-loosening to modern intelligent anti-loosening, from single-material applications to composite material use, all contributing to improving the reliability and safety of mechanical systems. We believe that nut anti-loosening technology will continue to improve in the future, providing stronger guarantees for the stable operation of mechanical equipment and enabling optimal performance in various application scenarios, creating more value for human production and life.