The best screws for MDF
Medium Density Fibreboard (MDF) To ensure connected sturdiness and durability, it is essential to choose the right screws. Based on a web search, here are some recommended types of quality screws for MDF:
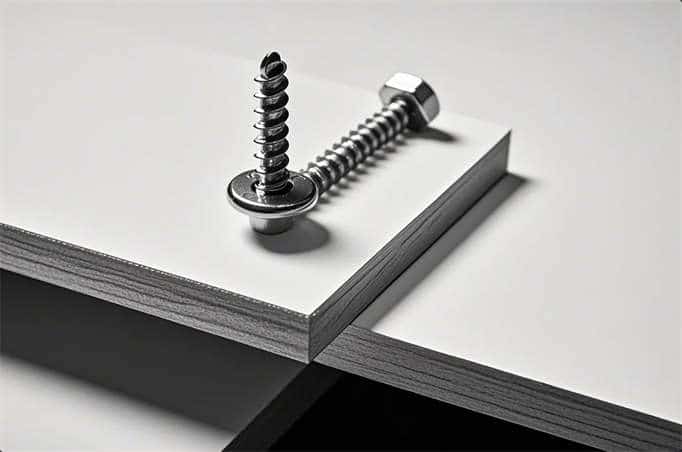
Wood Screws: wood screws are mainly used for the smooth coupling of wood materials, including MDF. They are commonly used for wood slag plywood, MDF, softwood and mahogany. Wood screws come in many different types and configurations, such as screws that avoid wood splints, double threads that turn screws effectively with screw tips that don’t cut holes ahead of time.
Self-tapping screws: Self-tapping screws are used in several different ways.
Self-tapping screws: Self-tapping screws are particularly suitable for dealing with metal, plastic, wood and plasterboard merchandise. They have a sharp or similar drill bit for screwing into metal parts but are also ideal for MDF.
SPAX® self-tapping screws for wood: SPAX® screws are widely used for interior, exterior, wood construction as well as window and door systems, especially for MDF boards and thick-walled board assemblies. They can be easily adapted to the material without the need for pre-set openings.
Plywood screws: Plywood screws are a heat-treated process suitable for assembling products with pneumatic tools and are mainly used for connecting and torquing wood panels, wood panels, to thin steel panels. They can replace the use of general wood screws to a certain extent.
When selecting screws, the size and type of screws should also be considered to ensure that they are consistent with the thickness of the MDF and the primary application. For example, for general use, #8 type screws are recommended, but for more detailed woodworking, #6 type screws may be needed
Choosing the right type and size of screws is critical to ensuring that the MDF is appropriately fixed.
What is the installation method for plywood screws?
The installation method for plywood screws generally involves the following steps:
Wall preparation: first, clear the wall to remove any dust or debris and ensure that the wall is dry and tidy, followed by assembly
Measuring and cutting MDF: Accurately measure the wall specification and cut the MDF to the appropriate specification using a saw.
Cut the MDF into suitable sizes using a saw.
Apply adhesive: Apply strong adhesive on the reverse side of the MDF or directly on the wall where the panels are to be placed.
Placement of panels
Placement of panels: Carefully place the MDF on the wall, slowly and firmly pressing from one corner to ensure excellent bonding.
Fixing with screws: for better stability.
Fixing with screws: To improve stability, fix the MDF to the wall with screws, especially if the adhesive is insufficient.
Decorative edges: Use decorative edges.
Decorative edges: To make the MDF look neat, cover the edges and joints with decorative edges or mouldings.
Decoration
During installation, the following points should also be noted:
Screws 15mm from the outside of the board, 50mm from the corner of the board parts, screws spaced about 180m ~ 200mm
Before guiding the board, according to the keel, according to the keel separation in the surface of the line, in the head of the nail over the part of the drilling a shallow pit, to ensure that the screws assembled surface neatly, the screw head sunk into the board, below the surface of the layer is not more than 0.5mm.
The head of the screw is sunk into the board, not more than 0.5mm below the surface. Fix the board slowly from the middle, and then fix the periphery.
Fix the plate slowly from the middle, and then fix the periphery. The gap between the board and the board is not less than 5mm, and the deformation joints are left at 10m~15m intervals on the top surface of large long aisles.
The gap between the boards is less than 5mm. These steps and precautions are conducive to ensuring that the plywood screws are assembled sturdily and beautifully.
Screw interval of gypsum board
The screw spacing of the gypsum board is generally determined according to the specific application scenario and the type of gypsum board. Here are some specific recommended intervals:
Ceiling use: Gypsum board is used for general ceilings, and the screw spacing is generally recommended to be 15 to 20cm.
Nail and board spacing: Nail and board spacing is not less than 15mm; nail spacing of 150 to 170mm is appropriate
Nail and board spacing: Nail and board spacing is at least 15mmat least 15mm, and nail spacing is 150~170mm.
The interval of self-tapping screws: When the gypsum board is fixed with a light steel keel, the interval of self-tapping screws is 200mm outside the board and 300mm in the board.
Self-tapping screw interval
Gypsum board: self-tapping screw interval around the gypsum board should not be greater than 200mmmm; self-tapping screw interval should not be greater than 300mm
Gypsum board: the interval of self-tapping screws around the gypsum board should not be greater than 200mmmm; the interval of self-tapping screws should not be greater than 300mmmm.
Curve target and straight-line orientation: curve trend refers to the self-tapping screw interval along the angle of the horizontal support keel should not be greater than 100mm. Straight line trend refers to the self-tapping screw interval along the angle of the secondary keel should not be greater than 150mm.
The linear trend is that the self-tapping screw interval along the angle of the secondary keel should not be greater than 150mm.
Such recommended intervals can be used as a reference for gypsum board assembly, but the specific installation specification may also be subject to various factors, such as gypsum board specifications, material strength, and load requirements. In daily work, to ensure safety and sturdiness, it is proposed to correct the interval in time with the actual situation or consult professional engineers.
How much is the spacing of plasterboard fixing screws?
The spacing of gypsum board fixing screws generally follows the following criteria:
Peripheral screw spacing: gypsum board peripheral screw spacing shall not be greater than 200mm
Intermediate section screw spacing: intermediate section screw spacing shall not be greater than 300mm.
Distance between the screws and the edge of the board
Distance between the screws and the edge of the board: the distance between the screws and the edge of the board should be 10~16mm.
The distance between the screws and the edge of the board
The panel wrapped outside the board and the interval between the screws: panel wrapped outside the board selection of 10mm ~ 15mm is appropriate, and cutting the board outside 15mm ~ 20mm is appropriate.
The interval between self-tapping screws
Self-tapping screws interval: self-tapping screws interval 150mm ~ 170mm is appropriate.
The interval of self-tapping screws is 150 mm~170 mm.
This kind of interval standard is helpful to ensure the solid installation of the gypsum board and the stability of the structure. The interval should be corrected in the field construction according to the actual design points and field specifications.
Best screws for MDF
When fixing Medium Density Board (MDF), it is vital to choose the right type of screws to ensure connected sturdiness and durability. Below are MDF recommendations for these quality screw types, including their specifications, procedures and experience:
1. SPAX® Self-Tapping Screws for Wood
Specifications:
SPAX® screws are available in a variety of sizes to meet different installation requirements
The length of the screws usually varies from a few millimetres to several tens of millimetres to accommodate different thicknesses of MDF boards.
The diameter of the screws also varies, with standard screw diameters varying. Screw diameters also vary, commonly 3.5mm, 4mm, 5mm, etc.
Operating Procedure:
SPAX® screws can go directly over the MDF boards without having to make holes earlier.
The SPAX® screws can go straight through the MDF board without having to cut the holes earlier. Turn the screws clockwise with an electric screwdriver or drill until the screw head is aligned with the surface.
The screw head is aligned with the surface. With rigid fibreboard, SPAX 4CUT and SPAX CUT screws have a precise positioning service, reducing the time spent on the job.
Splicing results:
SPAX® screws are firmly attached to the MDF board and can withstand high tensile forces and pressures.
The SPAX® screws are firmly attached to the MDF board and can withstand high tension and pressure. The unique design of the screws ensures high torque torque in hard plywood without damaging or distorting the material.
The SPAX® WIROX and YELLOX coatings provide additional corrosion protection for indoor and outdoor applications.
2. Plywood Screws
Specifications:
Plywood screws are generally heat-treated to enhance their hardness and durability.
Plywood screws are generally heat-treated to enhance their hardness and durability. The length and diameter of the plywood screws are specified according to the business needs, and the standard lengths are 16mm, 25mm, 40mm, and so on.
The standard lengths are 16mm, 25mm, 40mm, etc. Operation steps:
Plywood screws can be assembled directly with pneumatic tools without pre-set holes.
The plywood screws can be assembled directly with pneumatic tools without pre-setting the holes. The top design of the screws facilitates quick enquiry and drilling and reduces the installation simplicity.
The plywood screw design reduces the risk of cracking when using redwood.
Splicing effect:
Plywood screws are more effective in joining and torquing wood panels and can replace regular wood screws
The heat treatment of the screws makes them stronger when tightened and improves the stability of the joint.
The screws can be used as a substitute for general wood screws. Because of the sharp screw, it can achieve fast drilling and improve efficiency.
3. Plywood Screws with Claw Cut End
Specification:
Claw-cut end plywood screws are an improvement of general plywood screws.
The length and diameter of the screws are by the actual conditions. The size and diameter of the screws are specified according to the exact business needs to adapt to different thicknesses of the MDF board.
The length and diameter of the screws are specified according to actual business needs to accommodate different thicknesses of MDF board. Operation steps:
The design of the Claw Cut End Plywood Screw optimises the screw in pursuit of higher punching speeds.
The claw design of the screw favours the reduction of the risk of cracking during the use of mahogany.
The use of pneumatic tools allows for quick installation without pre-setting the opening.
Using a pneumatic tool allows for quick installation without pre-setting the holes. Assembly results:
The assembly result of the mahogany Liga claw cut end plywood screws is better than that of standard screws, which reduces the chance of dry cracking.
The screws are assembled better than ordinary screws, reducing the chance of dry cracking. High drilling speeds and precise positioning of the screws increase the efficiency of the installation.
The screws are heat-treated and sharpened. The heat treatment process of the screws and sharp screws ensures a strong and safe connection.
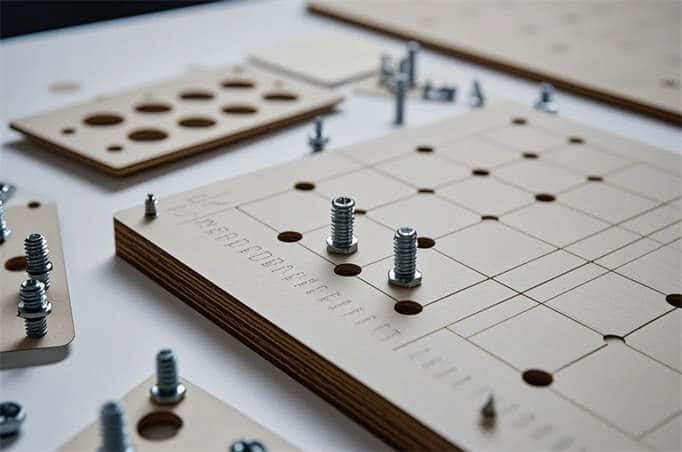
4. Screw and nuts fit
Specification:
Screws are generally large and long and need to withstand large loads.
Screws are generally large and long and need to withstand large loads. The specifications of screws include diameter and length, typically the diameter of about 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, etc.
The specifications include diameter and length, generally about 6mm, 8mm, 10mm in diameter, etc. Operation steps:
Equipment screws must be in advance in the MDF board to open the hole and to assist the nut application
Use a spanner or screwdriver to tighten the nuts on the machine screws to fix the MDF boards
When it is time to disassemble and replace the new, the composition of screws and nuts provides convenience
Assembly effect:
The composition of screws and nuts provides a firm fixing force suitable for light load application scenarios.
The screw and nuts composition provides a firm fixing force and is suitable for light load application scenarios. This installation procedure reduces the risk of damage to the MDF boards during installation, as the holes have to be cut in advance.
The screw and nut combination provides a firm fixing force in light-duty applications. The combination of screws and nuts is helpful in situations where frequent disassembly and reassembly is required.
5. Self-tapping screws
Specifications:
Self-tapping screws are generally smaller and shorter, with lower loads.
Self-tapping screws are generally smaller and shorter, with lower loads. According to the business needs to specify the length and diameter of the self-tapping screws, the general diameter of about 3.5mm, 4.5mm and so on.
The operation steps. Operation steps:
Self-tapping screws can directly attack the MDF board; opening the hole earlier is unnecessary.
Using an electric screwdriver or drill, rotate the self-tapping screws clockwise until the nail head is level with the surface.
The self-tapping screws are suitable for applications with light loads that do not require frequent dismantling.
The self-tapping screws are suitable for applications with light loads that do not require frequent disassembly. Assembly effect:
Self-tapping screws on MDF boards are easy, convenient to assemble, and suitable for fixing light structures.
Self-tapping screws are easy to assemble on MDF boards and suitable for fixing light structures. Due to their small size, their appearance is relatively hidden, making them ideal for aesthetic provisions.
The self-tapping screws are suitable for aesthetics regulations. Although the fixing power of self-tapping nails is not as strong as that of machine screws, they are sufficient for most interior decoration and furniture assembly.
The following is a summary of the selection of suitable MDF nails. In summary, when selecting screws ideal for MDF, attention should be paid to the type of screws, specifications, operating procedures and installation results. Self-tapping screws for SPAX® wood, plywood screws, claw-tailed plywood screws, machine screws with nuts and self-tapping screws are all good choices. Each screw has unique characteristics and application scenarios.
Choosing the correct type of screws can ensure that the MDF boards are fixed firmly and beautifully. In practice, the most suitable screw type should be selected according to the specific installation requirements and load criteria.
What is the difference between SPAX® screws and plywood screws?
SPAX® screws and plywood screws are two different types of standard parts, each with unique characteristics and primary applications. Below are the main differences between the two:
Material and Surface Finish:
SPAX® screws are generally made of steel and are surface hardened for durability and corrosion resistance
They may have a WIROXX® or YELLOX® surface treatment, which does not have a hexavalent chromium high corrosion-resistant surface coating.
Plywood screws are also heat-treated products suitable for pneumatic tool assembly and are mainly used for joining and tightening of wooden panels
Plywood screws are also heat-treated for pneumatic tool assembly. The exterior is generally silver in colour, with a single thread spiralling upwards, and generally complete teeth
Design Features:
SPAX® screw design can easily be according to the material, especially mahogany material, without pre-set openings.
They are available with precise positioning services such as SPAX 4CUT and SPAX CUT, which can shorten the time to work.
Plywood Screws Plywood screws are an improved thread design in pursuit of higher drilling speeds to handle mahogany applications that are prone to cracking.
Plywood Screws Claw-cut end plywood screws are an improvement of the general plywood screws, starting with the screw thread design.
The claw-type cut end plywood screw is an improved product of general plywood screws, first improved from the screw thread design. Primary Uses:
SPAX® screws are widely used in interior, exterior, timber frame, and window and door systems, including floors, ceilings, walls, furniture, staircases, kitchens, bathrooms and more.
Plywood Screws. Plywood screws are widely used in furniture processing, cabinetry, and other fields, and its wood and thin steel plate connection and screwing.
Screw Thread Type:
SPAX® screws may be partially screwed or fully screwed, depending on the product model and project requirements
Plywood Screws. Plywood screws are generally full-threaded and come in a variety of sizes, such as 3mm, 3.5mm, 4mm, 4.5mm, 5mm, 6mm, etc.
Head Shape and Slot Type:
SPAX® screws are available in countersunk head design, and the push-slot type may be hexagonal or cross-slotted Z (Pozidriv).
Plywood Screws. Plywood screws have a countersunk head, semi-countersunk heads, round mouths and other designs; the slot type has a cross slot (PHILLIPS), metric slot (POZI), square slot (SQURE), plum blossom grooves (TORX) and so on.
SQURE, TORX, etc. Overall, SPAX® screws and plywood screws are both self-tapping screws, but SPAX® screws place more emphasis on outdoor and mahogany material tightening, while plywood screws are more used to connect and tighten wood panels. Both differ in material, surface treatment, design features, primary use, screw and head design.
What is the difference between the use of self-tapping screws and machine screws with nuts on MDF boards?
There are several key differences between the use of self-tapping screws and machine screws with nuts on MDF (medium-density board) boards.
Different types of screw threads:
Self-tapping screws screw teeth are more expansive; the tooth angle is generally less than 60 degrees, and screw teeth are marked ST * / *.
The threads are marked ST*/*. This design promotes the self-tapping nail to form its screw in the material when screwed in, without the need for earlier holes and attacks.
Mechanical screws (machine screws) have narrow screws with a 60-degree tooth angle, and the screws are marked M*/*
The screw is marked M*/*. Screws need to be applied with a nut, or the hole has to be cut and attacked in advance on the MDF board to produce a screw thread.
The method of operation is different:
Self-tapping screws can be screwed directly into the MDF board without the need for additional nuts or prior tapping.
The screwing process is different. During the screwing process, the self-tapping screws form their threads into the material to secure it.
Screws generally need to be used in conjunction with a nut, or a hole must be made in the MDF board and tapped in advance to create a screw thread, which can then be tightened.
The screws can only be tightened after the hole is made and tapped on the MDF board. Different main uses:
Self-tapping screws are suitable for MDF boards and other non-metallic or soft metal materials; they have low joint strength but are easy to install; no need to punch holes in advance.
It has low coupling strength but is easy to install, so drilling holes in advance is unnecessary. Screws are suitable for general joint strength requirements of high places and must be punched and tapped in advance.
Screws Different tightening effect:
The tightening effect of self-tapping screws lies in the material in the formation of the screw and may not be as good as the tightening effect of equipment screws and nuts, especially in the case of larger loads.
Screws, when used in conjunction with nuts, provide a powerful tightening force for applications that require a high degree of tension or pressure to be applied.
The Ease of assembly varies:
Self-tapping screws can be screwed directly into the material, making the installation process easier and more convenient.
The installation process is more straightforward and more convenient. Screws and nuts require additional drilling and tapping, or additional nut components, making the installation process more complex.
The installation process is more complicated. Generally speaking, the main difference between the use of self-tapping screws and machine screws on MDF boards lies in the type of screw, operation method, primary purpose, tightening effect and Ease of installation. Self-tapping screws are more suitable for quick installation and soft material fixing, while machine screws and bolts are suitable for areas with stronger tightening forces and precise couplings.